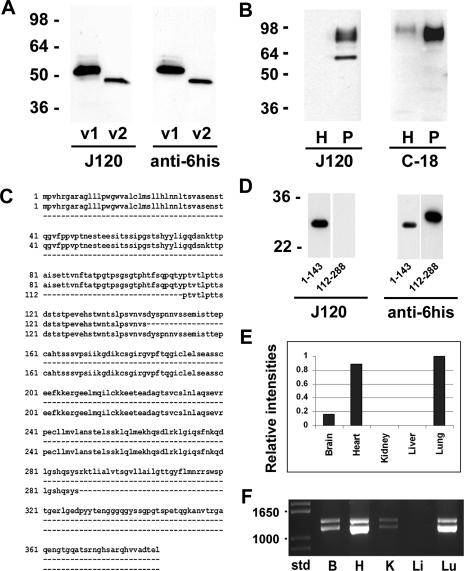
Fig. 7.
Expression of CD34 isoforms. A: Western blot analysis of recombinantly expressed rat CD34 variant 1 (v1) and variant 2 (v2). Left blot was probed with MAb J120; right blot was probed with anti-6his. Both recombinant proteins run at a slower electrophoretic mobility than predicted from their deduced amino acid sequence. B: Western blot analysis of normal rat lung homogenates (H) and endothelial cell plasma membrane (P). The blot shown at left was probed with MAb J120; the blot at right was probed with a polyclonal antibody to the cytoplasmic tail of CD34. Two bands were seen in the blot probed with J120, whereas only the higher-molecular-weight signal was seen in the blot probed with the antibody to the cytoplasmic domain, indicating that the lower-molecular-weight band represents rat CD34 variant 2. C: alignment of the full-length amino acid sequence of rat CD34 (top lines) with the cloned partial sequences of the extracellular domain encompassing amino acids 1–143 (middle lines) and amino acids 112–288 (bottom lines). D: Western blot analysis of recombinantly expressed partial amino acid sequences 1–143 and 112–288. The Western blot strips at left were probed with J120; strips at right were probed with anti-6his to detect the his tag on the amino termini of the recombinantly expressed protein fragments. E: QPCR analysis of CD34 mRNA in rat brain, heart, kidney, liver, and lung. The intensity of the normalized signal from rat lung was arbitrarily set at a value of 1; the intensities in the other organs are relative to the lung value. F: RT-PCR analysis of CD34 mRNA showing the presence of variant 1 (bottom band) and variant 2 (top band) in rat brain (B), heart (H), kidney (K), and lung (Lu) but not in liver (Li). Molecular weight standards are shown at left.