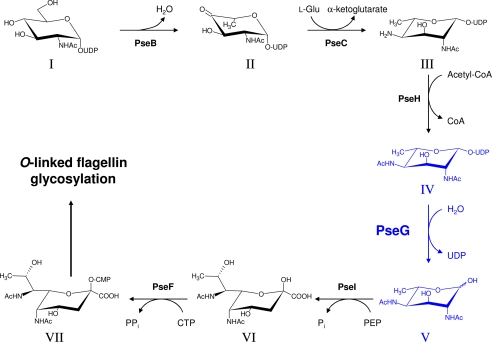
FIGURE 1.
Role of PseG within the CMP-pseudaminic acid biosynthetic pathway of C. jejuni and H. pylori. The biosynthetic step involving PseG is highlighted in blue. The enzymes and biosynthetic intermediates of the CMP-pseudaminic acid pathway are, in the following order, PseB (Cj1293/HP0840), NADP-dependent dehydratase/epimerase; PseC (Cj1294/HP0366), pyridoxal phosphate-dependent aminotransferase; PseH (Cj1313/HP0327), N-acetyltransferase; PseG (Cj1312/HP0326B), NDP-sugar hydrolase; PseI (Cj1317/HP0178), pseudaminic acid synthase; PseF (Cj1311/HP0326A), CMP-pseudaminic acid synthetase; and I, UDP-GlcNAc; II, UDP-2-acetamido-2,6-dideoxy-β-l-arabino-hexos-4-ulose; III, UDP-4-amino-4,6-dideoxy-β-l-AltNAc; IV, UDP-2,4-diacetamido-2,4,6-trideoxy-β-l-altropyranose; V, 2,4-diacetamido-2,4,6-trideoxy-l-altropyranose; VI, pseudaminic acid; and VII, CMP-pseudaminic acid. Here, PEP refers to phosphoenolpyruvate. Pyranose rings are shown as their predominant chair conformation in solution as determined from nuclear Overhauser effects and JH,H coupling constants (13).