Figure 3. XProfilin2 is required for gastrulation.
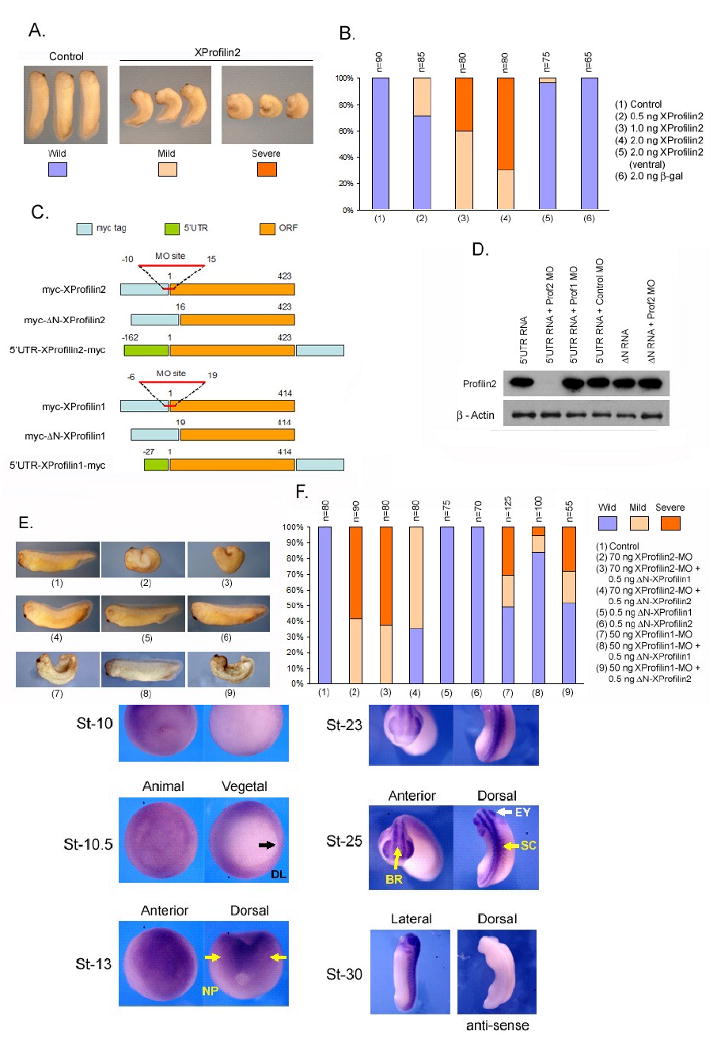
(A) Injection of XProfilin2 RNA dorsally but not ventrally inhibits gastrulation with the resulting embryos having open neural folds and reduced anterior structures (Severe) or delayed blastopore closure and a curved/bent axis (Mild). (B). Quantitation of the phenotypic results from overexpression studies of XProfilin2. Number of embryos scored (n) is shown at the top of each bar. (C) Schematic representation of the XProfilin2 constructs and targeted-Morpholino site. (D). Injection of the XProfilin2 MO but not XProfilin1 MO or a control MO inhibits translation of Myc-tagged 5′UTR-XProfilin2. The ΔN-XProfilin2 cDNA lacking the XProfilin2 MO recognition sequence is insensitive to the effects of the XProfilin2 MO. (E). Injection of XProfilin2 MO inhibits gastrulation and results in a similar gastrulation-defect phenotype as overexpression of XProfilin2 RNA (see A). This phenotype is reversed by injection of ΔN-XProfilin2 but not ΔN-XProfilin1 (F). Quantitation of phenotypic results of XProfilin2-depletion studies. Number of embryos scored (n) is shown at the top of each bar.
