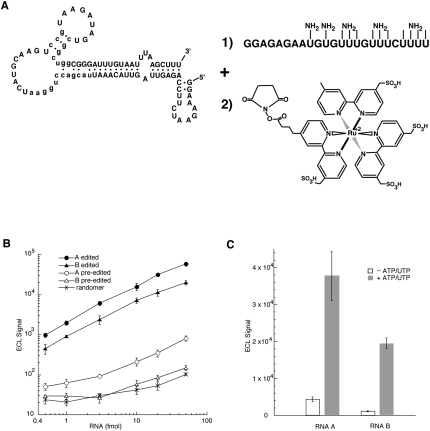
FIGURE 3.
Characterization of the ECL assay. (A) Labeling the selected RNAs with the ruthenium complex. An RNA containing 5-(3-aminoallyl)-uridylates (NH2) was ligated to the 3′-end of the selected RNAs using DNA ligase and the appropriate DNA splint (Moore and Sharp 1992). The RNA was subsequently reacted with an N-hydroxysuccinimide ester of the ruthenium complex. (B) The indicated quantities of edited RNA A (●), edited RNA B (▲), pre-edited RNA A (○),pre-edited RNA B (Δ) and the starting randomer (×) were incubated with the streptavidin-coated microtiter plates, and after washing and scanning, the ECL was detected (n = 4). (C) The signal-to-background ratio of the complete ECL editing reaction was determined for reporters A (n = 6) and B (n = 8) by treating the pre-edited RNAs with editing extract both in the presence (gray) and absence (white) of the essential nucleotide cofactors. The indicated ECL units were detected after washing and scanning of the plate.