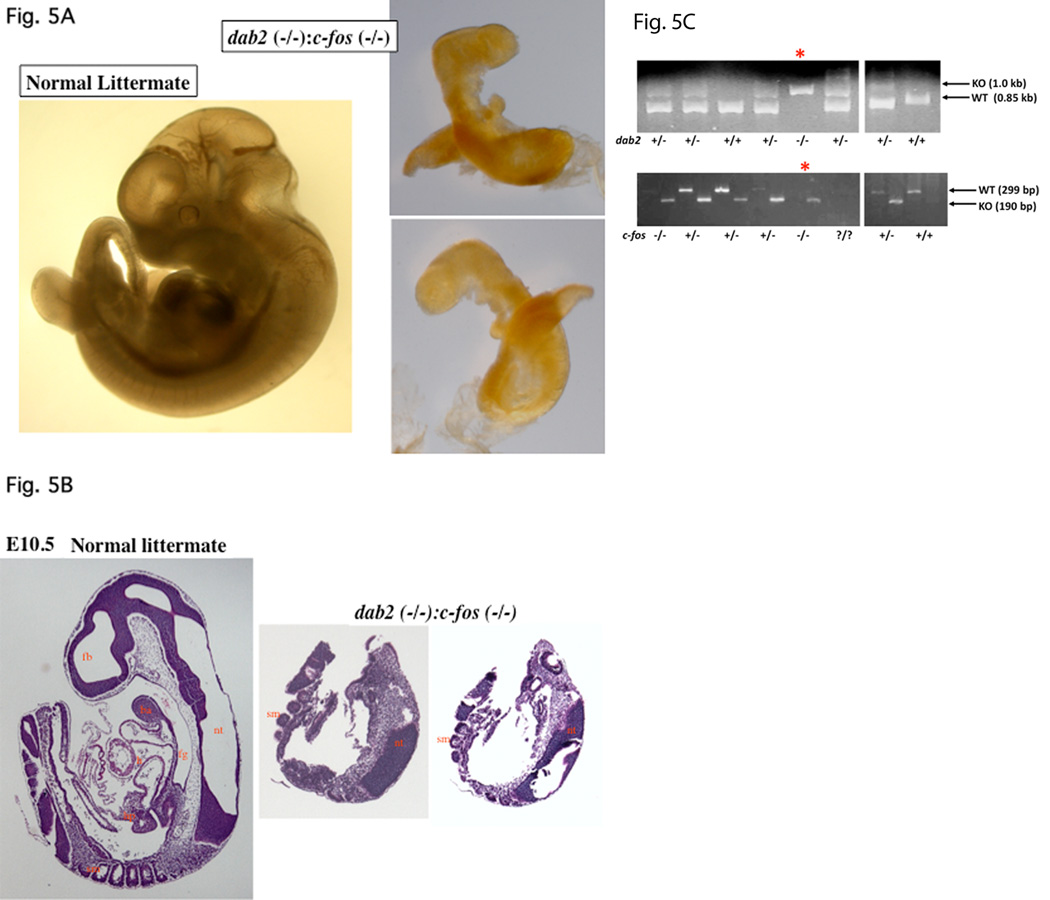
Fig. 5.
Delay of lethality to E10.5 of dab2 (−/−) embryos in the c-fos null background. Embryos from timed-mating between dab2 (+/−):c-fos (+/−) mice were analyzed. Following photographing under a microscope, part of the embryonic tissues (often the extraembryonic tissues, the yolk sac) was used for genotyping by PCR. (A) A pair of normal and abnormal (identified as dab2 (−/−):c-fos (−/−)) embryos is shown. The abnormal embryo was photographed on both sides to show a lack of apparent organs. (B) The abnormal E10.5 embryo was sectioned and stained with H&E to compare with a wildtype littermate control. The abnormal embryo was sectioned through and two representative sections around the midpoint are shown. (C) A small fragment of each embryo was used in PCR amplification of dab2 (wildtype, 1.0 kb; knockout, 0.85 kb) and c-fos (wildtype, 299 base pair; knockout, 190 base pair) genes for genotyping. The morphologically abnormal embryo, indicated by “*”, was identified as dab2 (−/−): c-fos (−/−) genotype. Abbreviations in Figures: ba, branchial arch; ca, cardiac mesoderm; en, endoderm; fg, foregut diverticulum; h, heart; hp, hepatic primordial; nt, neural tube; ov, optic vesicle; sm, somites; st, septum transversum.