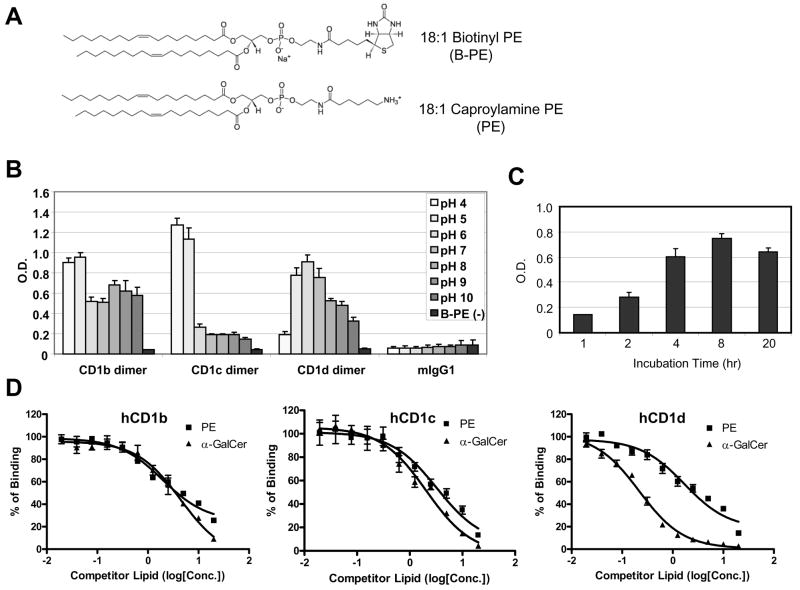
Fig. 3. Competitive ELISA assay to detect the binding of the lipid to hCD1 molecules.
A) Chemical structures of lipids used in the competitive ELISA assay. 18:1 Biotinyl PE was used as a detector lipid and 18:1 Caproylamine was used as a competitor lipid. B) Binding of Biotinyl PE to human CD1 molecules in different pH conditions. The pH of phosphate buffer saline was adjusted with HCl or NaOH to the indicated pH. Biotinyl PE (1μg/mL) was incubated with hCD1 dimers in the indicated pH conditions for overnight at 37°C in ELISA plates coated with anti-mouse IgG Fc antibody. mIgG1 is mouse isotype control IgG1, which has the same structure as hCD1 dimers except for the β2m-CD1 portion. B-PE (−) is the well without biotinylated PE at pH 7. The assay was done in triplicate and the error bars indicate Standard Deviation (SD). C) Kinetics of Biotinyl PE binding to hCD1d dimer. Biotinyl PE (1μg/mL) was incubated with hCD1 dimers for the indicated time at 37°C in ELISA plates coated with anti-mouse IgG Fc antibody. The assay was done in triplicate and the error bars indicate Standard Deviation (SD). D) Results of the competition ELISA assays with PE or α-GalCer. Biotinyl PE (2μg/mL) was incubated with hCD1b (left), hCD1c (middle) or hCD1d (right) dimer in the presence of the competitors at the indicated concentration in ELISA plates described in C). The assays were done in triplicate and the error bars indicate Standard Deviation (SD). X-axis represents concentration of a competitor lipid (log [μM]).