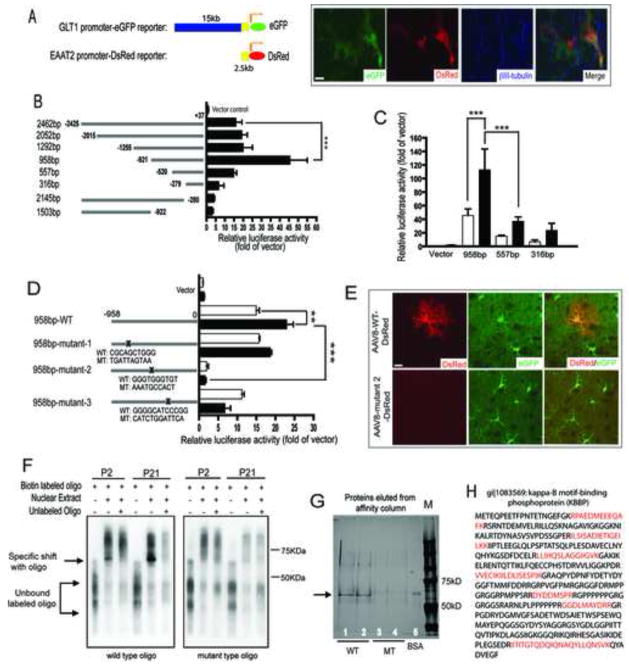
Figure 3. Recruitment of Kappa B-motif binding phosphoprotein (KBBP) to GLT1 promoter is required for its activation.
A. A 2.5kb of human EAAT2 promoter is sufficient for neuronal stimulation in mouse astrocyte environment. The EAAT2 2.5kb promoter-DsRed reporter and GLT1 genomic promoter-eGFP reporter were both activated in astrocytes following co-culture with neurons identified by βIII-tubulin immunostaining. B. Identification of the regions essential for the basal activity of human EAAT2 promoter by serial deletion of human EAAT2 promoter (n=5–7). C. Promoter sequence from −958bp to −557bp is mainly responsible for neuron-dependent GLT1 promoter activation in primary astrocytes (n=4–8). □=astrocytes alone; ■=astrocytes and neurons. D. Mutagenesis of GGGTGGGTGT from −688bp to −679bp almost completely abolished basal and neuron-dependent GLT1 promoter activity in vitro (n=6–8). For luciferase assay, luciferase promoter reporters were first electroporated into cultured astrocytes and then freshly prepared neurons were plated on the top of transfected astrocytes. β-galactosidase was co-transfected for normalization. E. Mutagenesis of GGGTGGGTGT from −688bp to −679bp abolished GLT1 promoter activation (indicated by DsRed reporter expression) in astrocyte in vivo during early post-natal development. Astrocytes were identified by positive eGFP expression (20–30 astrocytes examined per serial section/mouse for total 4 mice each). F. Mutagenesis of cis-element GGGTGGGTGT abolished its specific binding to nuclear factors during GLT1 promoter activation in early post-natal development. G. Affinity purification by using wild type oligo GGGTGGGTGT but not the mutant oligo found unique nuclear protein from P21 mice cortex nuclear extracts. H. Trypsin digestion and LC/MS/MS identified Kappa B-motif binding phosphoprotein (KBBP) that specifically binds to GGGTGGGTGT. The red-colored amino acid sequences are small peptide sequences identified from LC/MS/MS that also match with KBBP sequence in NCBI.