Figure 2. mGluR2 transmembrane domains 4/5 mediate association with 2AR.
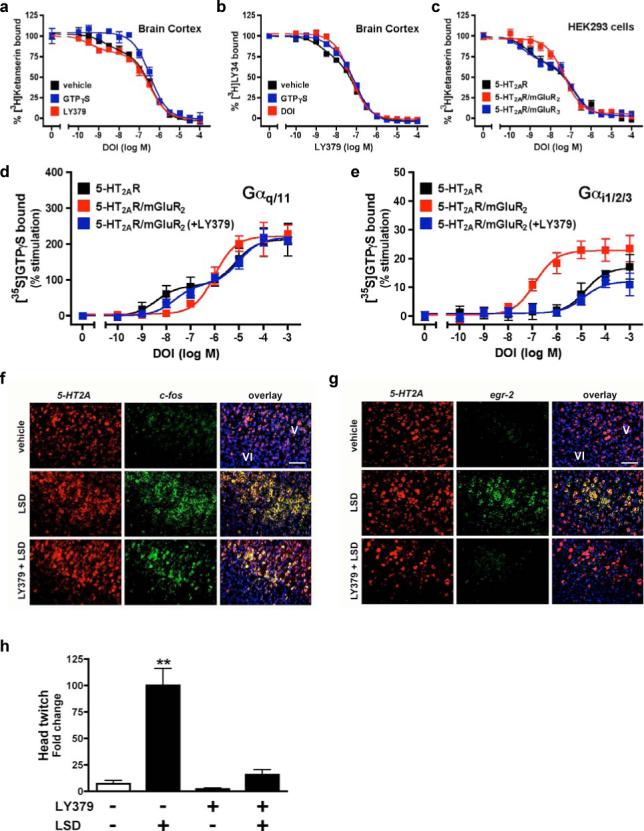
a, mGluR2/mGluR3 chimeras studied. b, c-myc-2AR and HA-mGluR2/mGluR3 chimera co-immunoprecipitations. Cells separately expressing each construct were also mixed. c, 2AR competition binding in cells stably expressing 2AR and transfected with mGluR2/mGluR3 chimeras. d, FRET in cells expressing 2AR-eCFP and either mGluR2, mGluR3 or mGluR3ΔTM4,5 chimera, all tagged with eYFP. Pseudo-colour images represent normalized values (FRETN). eCFP + eYFP (n=19); 2AR-eCFP + mGluR2-eYFP (n=43); 2AR-eCFP + mGluR3-eYFP (n=31); 2AR-eCFP + mGluR3ΔTM4,5-eYFP, (n=27). **p < 0.01; ANOVA with Dunnett's post hoc test. e, DOI-stimulated [35S]GTPγS binding in membranes followed by immunoprecipitation with anti-Gαq/11 (top panels), or anti-Gαi1,2,3 (bottom panels). Cells stably expressing 2AR were transfected with mGluR2, mGluR3 or mGluR3ΔTM4,5. The potency of DOI activating Gαi1,2,3 was significantly increased when the 2AR was co-expressed with either mGluR2 or mGluR3ΔTM4,5, an effect abolished by 10 μM LY379 (p<0.001 by F test). Data are mean±s.e.m. of three experiments performed in triplicate. f, Ribbon backbone representation of the transmembrane helices of the 2AR/mGluR2 heteromer model from the intracellular face.
