Figure 5. Suppression of LRP4 expression attenuates neuronal agrin binding, MuSK activation, and induced AChR clustering.
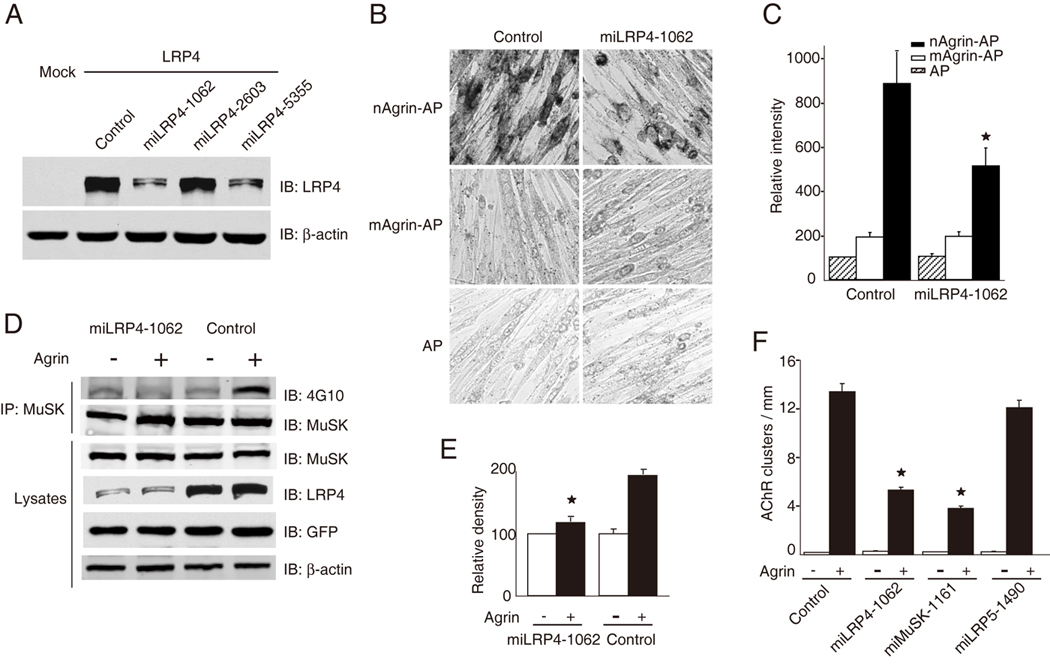
(A) Characterization of LRP4-miRNA constructs. HEK293 cells were transfected with LRP4 and LRP4-miLRP4 constructs or control miRNA that encoded scrambled sequence. Cell lysates were analyzed for LRP4 expression by immunoblotting with anti-LRP4 antibody. β-Actin was used as loading control. miLRN4-1062 was most potent in inhibiting LRP4 expression.
(B) Repression of LRP4 expression reduced neuronal agrin binding to myotube surface. C2C12 myotubes were transfected with control (scramble) miRNA or miLRP4-1062. Cells were incubated with AP, mAgrin-AP or nAgrin-AP, which was visualized in cell as described in Figure 3A.
(C) Quantitative analysis of data in B. Data shown were mean ± SEM. n = 6; *, p < 0.05 in comparison nAgrin-AP with control.
(D) MuSK activation by neuronal agrin was diminished in C2C12 myotubes transfected with miLRP4-1062. C2C12 myotubes were transfected with control miRNA or miLRP4-1062. 36 hr later, myotubes were treated without or with agrin for 1 hr and cells were then lyzed. MuSK was isolated by immunoprecipitation and blotted with the anti-phosphotyrosine antibody 4G10. Lysates were also blotted for MuSK, LRP4, GFP (encoded by miRNA constructs), and β-actin to indicate equal amounts of proteins.
(E) Quantitative analysis of data in D by ImageJ software (mean ± SEM, n = 3; *, P < 0.05 in comparison with control).
(F) Neuronal agrin-induced clustering of AChRs was inhibited in C2C12 myotubes transfected with miLRP4-1062. C2C12 myotubes were transfected by control miRNA, miLRP4-1062, miMuSK-1161, or miLRP5-1490. AChR clusters were induced by neuronal agrin and quantified as described in Experimental Procedures (mean ± SEM, n = 5; *, p < 0.05 in comparison with control). miMuSK-1161 and miLRP5-1490 were able to suppress expression of respective proteins in transfected cells (data not shown).
