Figure 6. Direct interaction between LRP4 and MuSK.
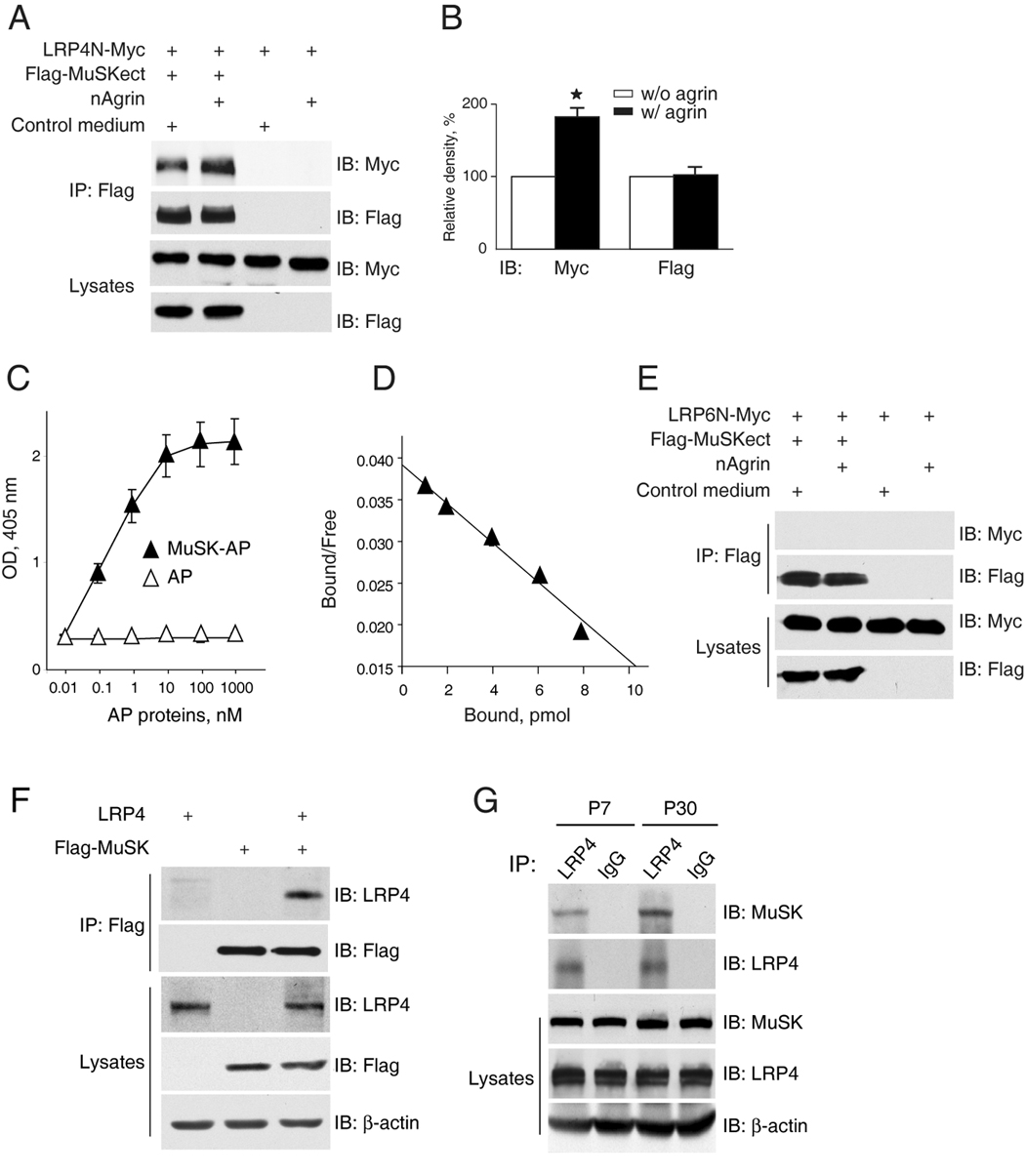
(A) Increased LRP4-MuSK interaction in the presence of neuronal agrin. Flag-MuSKect immobilized on beads were incubated with condition media of cells expressing the extracellular domains of LRP4 (LRP4N-Myc) or the empty vector (control) in the presence or absence of neuronal agrin. Precipitated LRP4 was analyzed by immunoblot with anti-Myc antibody. Reaction mixtures were also blotted directly for Flag and Myc to demonstrate equal amounts of proteins.
(B) Quantitative analysis of LRP4N-Myc and Flag-MuSK. Data shown were mean ± SEM, n = 3; *, p < 0.05 in comparison with the no-agrin group.
(C) Dose-dependent interaction between LRP4 and MuSK. Purified LRP4-Myc was coated on Maxi-Sorp Immuno Plates, which were incubated with MuSK-AP. Bound AP was measured with pNPP as substrate. Data shown were mean ± SEM. n = 4.
(D) Scatchard plot of data in C. Y axis represents the ratio of bound to free MuSK-AP whereas X axis represents the concentration of bound MuSK-AP.
(E) No interaction of LRP6 and MuSK extracellular domains. Experiments were done as in A except condition medium of cells expressing the extracellular domain of LRP6 was used.
(F) Co-immunoprecipitation of LRP4 and MuSK. HEK293 cells were transfected with LRP4 and/or Flag-MuSK. Lysates were incubated with anti-Flag antibody, and resulting immunocomplex was analyzed for LRP4 and Flag. Lysates were also probed to indicate equal amounts of indicated proteins.
(G) Interaction of LRP4 with MuSK in mouse muscles. Mouse muscles of indicated ages were homogenized, and homogenates were incubated with rabbit anti-LRP4 antibody or rabbit normal IgG. Precipitates were probed for MuSK and LRP4. Homogenates were also probed directly for MuSK, LRP4, and β-actin (bottom panels).
