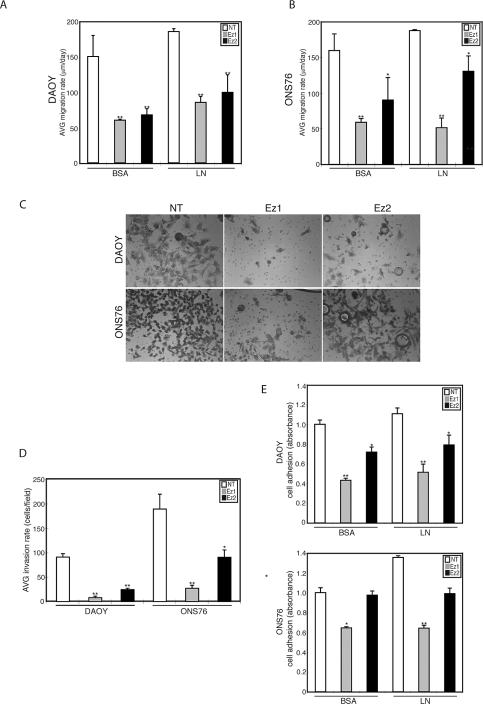
Fig. 3.
Effects of ezrin depletion on medulloblastoma (MB) cell migration, invasion, and adhesion. (A and B) MB cells transfected with ezrin small interfering RNA (siRNA) were seeded through a cell sedimentation manifold to establish a circular confluent monolayer on substratecoated wells (bovine serum albumin [BSA] or laminin [LN]). DAOY (A) and ONS76 (B) cells were incubated for 24 h, and images were used to measure migration. The average (AVG) migration rate was calculated as the change in the diameter of the circle circumscribing the cell population for a 24-h period. (C) Modified Boyden chamber invasion assay after transfection with ezrin siRNA in DAOY and ONS76 MB cell lines. After incubation for 24 h, the cells that migrated through the membrane were stained and representative fields were imaged. Abbreviations: NT, nontargeting siRNA; Ez1 and Ez2, two different ezrin knockdown sequences used. Magnification, ×200. (D) Invasion was quantified by counting cells. Ezrin siRNA significantly inhibited the invasion of MB cell lines. Columns represent the average (AVG) + SEM invasion rate (cells/fields). (E) Adhesion assay for MB cells tested on BSA and LN. Cells were seeded on 96-well plates coated with BSA or LN, incubated for 3 h, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, and then stained with crystal violet. The absorbance was measured at 595 nm (mean + SEM). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, versus control.