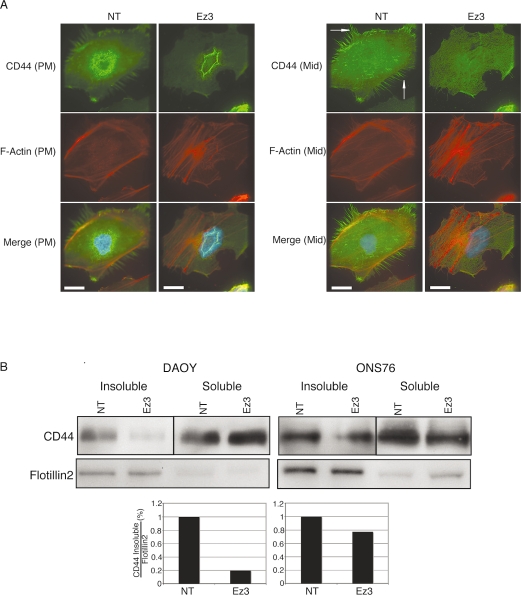
Fig. 4.
CD44 expression after transfection with ezrin small interfering RNA (siRNA). (A) Cells were seeded onto bovine serum albumin–coated or laminin-coated cover slips. After fixation, Texas red-X phalloidin and CD44 antibody were used to localize endogenous actin and CD44 by immunofluorescence. Images were acquired by serial focal planes to examine CD44 expression at the plasma membrane (PM, left) or a plane in the middle of the cell (Mid, right). Compared with control cells, ezrin knockdown reduced CD44 expression at filopodia and the plasma membrane in DAOY cells (arrows). Scale bars, 25 μm. (B) Top: Whole-cell lysates and Triton-soluble and -insoluble protein fractions were extracted from DAOY and ONS76 after transfection with ezrin siRNA. Protein (20 μg) was separated with sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and blotted onto an Immobilon-P polyvinyl difluoride membrane. CD44 protein was detected using an anti-CD44 antibody in each sample. Flotillin-2, a marker of the insoluble fraction, was used as a loading control. Bottom: Quantification by densitometry of a representative experiment. Abbreviations: NT, nontargeting siRNA; Ez3, ezrin siRNA.