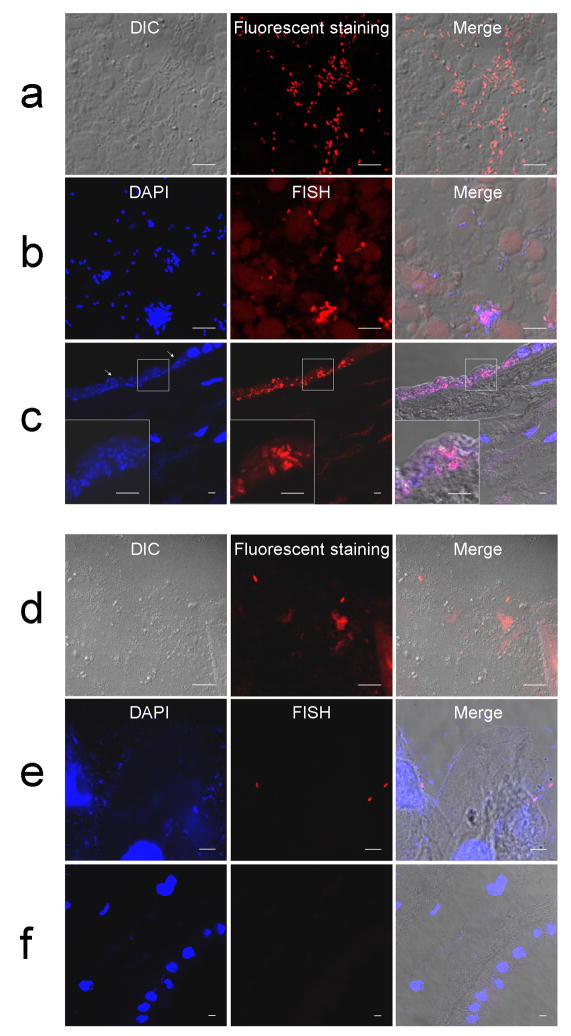
Figure 2.
Distribution patterns of bacteria detected by either bacterial 16S rRNA FISH using a EUB338 probe or fluorescent staining. (a–c) A case showing numerous rods in amniotic fluid pellets by fluorescent staining (a) and by 16S rRNA FISH (b). (c) 16S rRNA FISH of the chorioamniotic membranes showing bacterial invasion into amniotic epithelium. The invasion is largely restricted to amniotic epithelium. Cytopathic changes of amniotic epithelial cells with loss of nuclei are evident (arrows). (d–f) Another case showing scattered bacteria in amniotic fluid pellets by fluorescent staining (d) and 16S rRNA FISH (e) but not in the chorioamniotic membranes (f). Magnification ×630.