Figure 6.
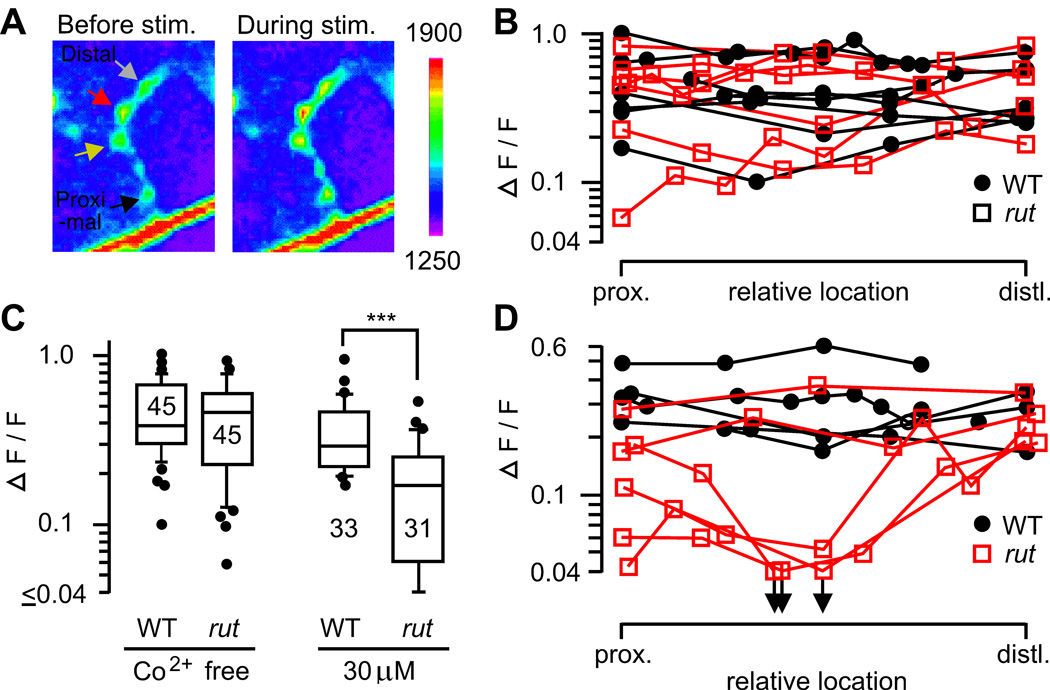
Uniformity of Ca2+ channel-dependent Ca2+ accumulation in motor terminal branches. A. Presynaptic Ca2+ accumulation was monitored with a Ca2+-sensitive green fluorescent protein, GCaMP, expressed in motoneurons (see Methods). Fluorescence intensities in WT presynaptic boutons before and during nerve stimulation (20 Hz, 5 s) are shown. B. Ca2+ accumulation along motor terminals in WT and rut. Note uniform amplitudes of ΔF/F within individual nerve terminals. C. Increased sensitivity of rut1 terminals to a Ca2+ channel blocker, Co2+. Peak ΔF/F during 20-Hz stimulation was significantly reduced by 30 µM Co2+ in rut but not in WT terminals (***, p < 0.001; t-test). D. Increased variation among rut terminals after partial Co2+ blockade (30 µM). The symbols in B and D represent the relative positions of individual boutons along the type Is terminal. Boutons along individual WT (filled circles) and rut (open squares) terminals are connected with line segments.