Figure 2.
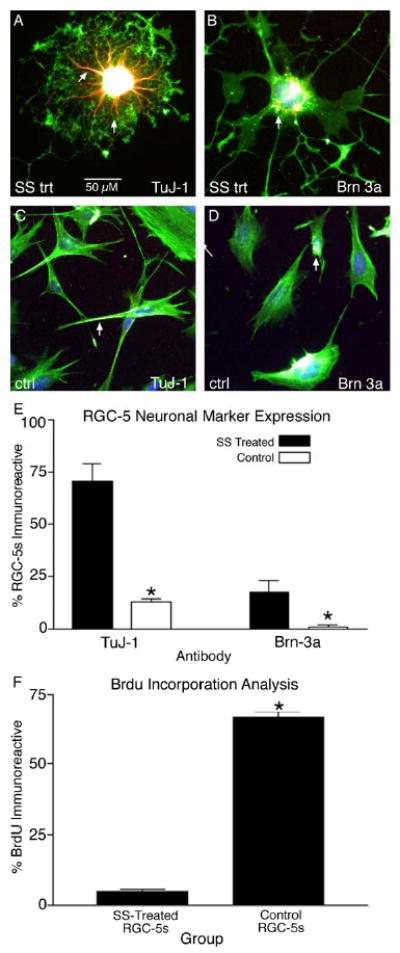
Staurosporine differentiation upregulates neuronal marker expression in RGC-5s. Differentiated RGC-5s were highly immunoreactive for the phenotypic neuronal marker TuJ-1 in the processes (A, arrows) and cell body. In addition, SS differentiated RGC-5s were immunoreactive for the RGC transcription factor Brn3a (B, arrow). In contrast, undifferentiated, control RGC-5s expressed TuJ-1 (C, arrow) and Brn3a (D, arrow) at relatively low levels. Quantification of the number of SS-treated RGC-5s expressing phenotypic markers revealed a significant increase from 13.0 ± 1.3 % (± S.E.M.) in control RGC-5s to 70.26 ± 8.37 % in SS differentiated RGC-5s for TuJ-1 (E, p < 0.0001). This trend was also observed for Brn3a expression patterns, with a significant increase from 1.06 ± 0.82 % of control RGC-5s expressing Brn3a to 17.36 ± 5.57 % of differentiated RGC-5s immunoreactive for Brn3a (E, p < 0.05). Finally, BrdU analysis revealed that only a small proportion of the differentiated RGC-5s incorporated BrdU (4.62 ± 0.76 %), a significant decrease from 66.7 ± 1.91 % of undifferentiated RGC-5s, (F, p < 0.0001).
