Figure 3.
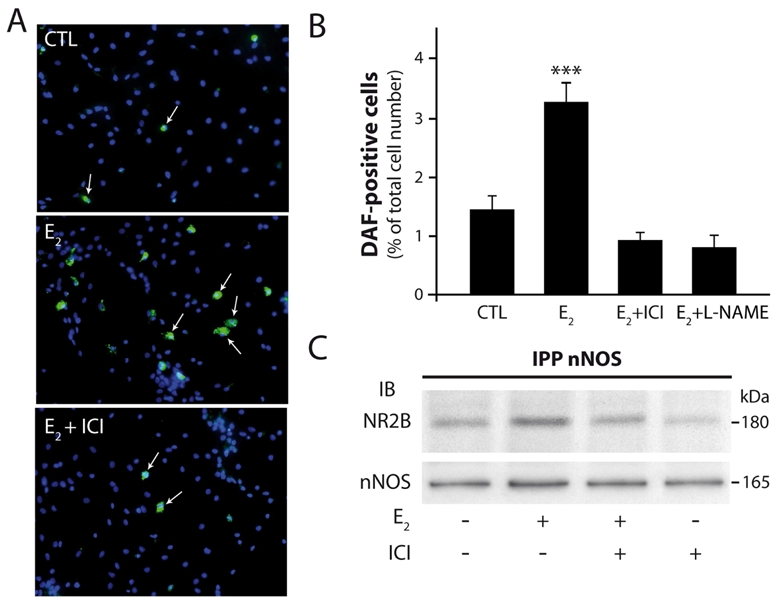
Estradiol stimulates NOS catalytic activity in hypothalamic preoptic neurons in vitro. Both estradiol-stimulated NO formation and nNOS/NR2B complex formation requires estrogen receptor activation in cultured neurons of the preoptic region. Neurons were treated with 17-b-estradiol (E2) 1 nM for 30 min and exposed to ICI 182,780 1 μM, a pure estrogen receptor antagonist, or to L-NAME 1 mM, a NOS inhibitor, for 30 min before this treatment. A, An example of fluorescent images of purified neurons loaded with the NO-sensitive dye DAF-FM (arrows) in control- (CTL) 17-b-estradiol- and 17-b-estradiol plus ICI 182,780-treated conditions (E2 + ICI). Scale bar, 40 μm. B, Summary graph showing that the pure estrogen receptor inhibitor ICI 182,780 and the NOS inhibitor L-NAME significantly reduced the amplitude of 17-b-estradiol-induced DAF fluorescent increase in neurons. ***, p < 0.001. Statistical differences were established using a one way ANOVA by the Student-Newman- Keuls multiple comparison test; n = 6–8 independent observations. C, ICI 182,780 Inhibits 17-b-estradiol-stimulated NR2B/nNOS complex formation in neurons of the rat preoptic region in culture. After treatment proteins were extracted and processed as indicated above in Figure 2. IPP, immunoprecipitation; IB, immunoblot.
