Figure 3.
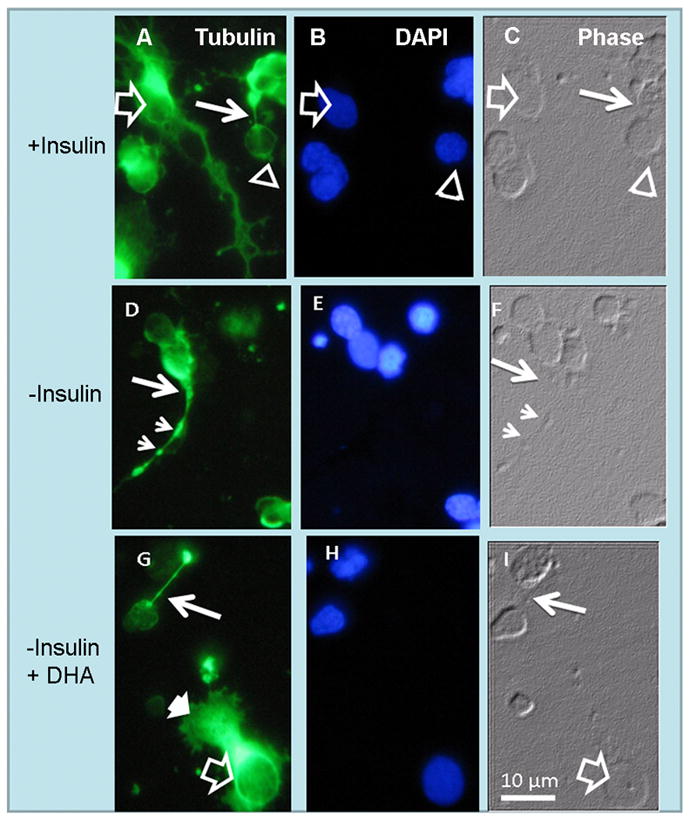
Anomalous development of axon cones in insulin-lacking photoreceptors. Phase (C, F, I) and fluorescence photomicrographs showing tubulin labeling (A, D, G) and nuclei (B, E, H) of amacrine neurons (open arrows) and photoreceptor (open arrowheads) in day 6 cultures. In the presence of insulin (A–C) photoreceptor axons showed normal “axon cones” (thin white arrows in A, C). Note the extensive neurite outgrowth in amacrine neurons (open arrows in A). Also note that in the absence of insulin (D–F) many photoreceptors developed wide axon cones (thin white arrows) and showed axons with scattered tubulin clumps (small arrowheads in D, F). DHA addition to insulin-lacking cultures (G–I) prevented the abnormal development of photoreceptor axon cones and allowed formation of lamellipodia (white arrowhead in G) in amacrine neurons, but could not reverse their lack of neurite outgrowth.
