Figure 4. Structural conservation of Spt4 and Spt5NGN domain.
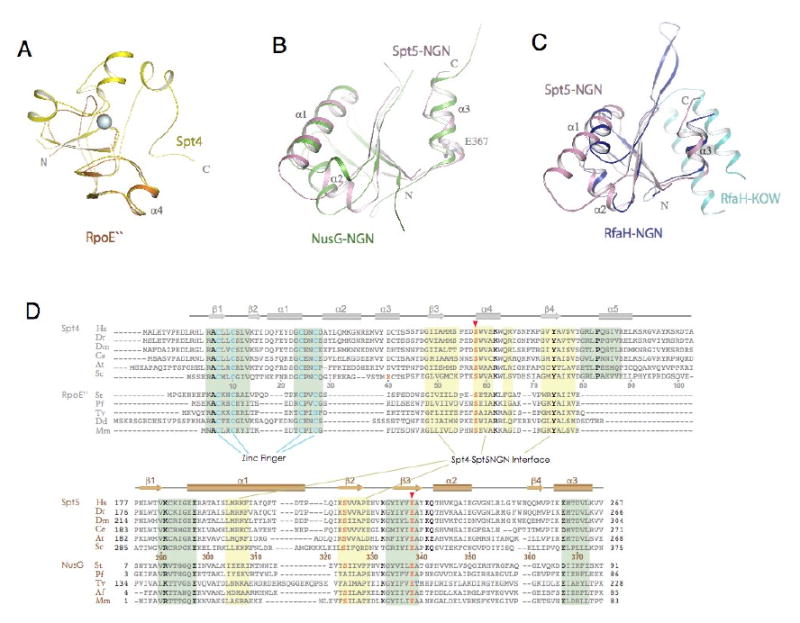
(A) Structural superimposition of Spt4 (yellow) with Pyrococcus furiosus RpoE″ (orange, pdb1ryq). (B) Structural superimposition of Spt5NGN domain with the Aquifex aeolius NusG (green, pdb1npp). (C) structural superimposition of Spt5NGN domain with the e.coli RfaH (pdb2oug, NGN in dark blue and KOW in light blue). (D) Alignment of representative Spt4 and Spt5 homologues. Residues that fall in the binding interface between Spt4 and the Spt5NGN domain are noted with a yellow background; residues that contribute to structural stability are noted by the green background. Highly conserved residues are depicted in bold type; residues in pink are involved in the acid-dipole interaction. Abbreviations: Hs, Homo sapiens; Dr, Danio rerio; Dm, Drosophila melanogaster; Ce, Caenorhabditis elegans; At, Arabidopsis thaliana; Sc, Saccharomyces cerevisiae; St, Sulfolobus tokodaii; Pf, Pyrococcus furiosus; Tv, Thermoplasma volcanium; Dd, Dictyostelium discoideum; Af, Archaeoglobus fulgidus; Mm, Methanococcus maripaludis;
