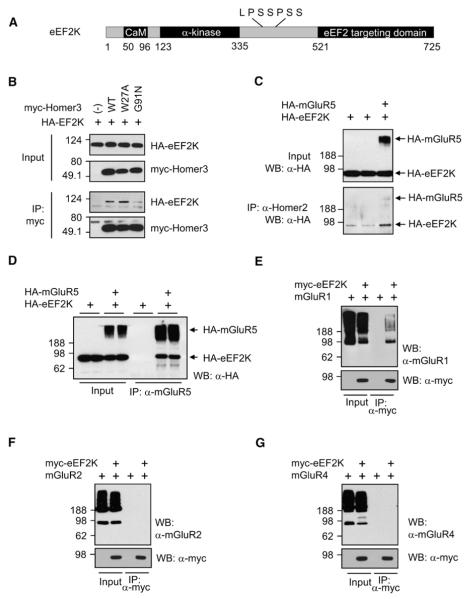
Figure 3. eEF2K Binds Homer and mGluR1/5.
(A) Schematic diagram of eEF2K. The N terminus of eEF2K contains a Ca2+/calmodulin (CaM) binding motif and an α-kinase domain. The C-terminal eEF2 targeting domain, which recruits the substrate, eEF2, is linked to the hyperphosphorylated internal region. Putative Homer binding site is shown above the diagram.
(B) Coimmunoprecipitation (co-IP) of eEF2K and Homer. HA-tagged (HA-) eEF2K was coexpressed with myc-tagged WT, W27A, or G91N Homer3 in HEK293T cells, and IP was performed with antimyc antibody. HA-eEF2K co-IPed with WT or W27A Homer 3 was coexpressed, but not with G91N Homer.
(C) mGluR5 increases the interaction of eEF2K and Homer. HA-eEF2K was transfected with or without HA-mGluR5. IP was performed by anti-Homer2 antibody, which IPed endogenous Homer2 protein. Western blot was performed using anti-HA antibody. Co-IP of HA-eEF2K was increased when mGluR5 was coexpressed.
(D) eEF2K co-IPs with mGluR5. HEK293T cells were transfected with HA-eEF2K with or without HA-mGluR5, and lysates were IPed with anti-mGluR5 antibody and blotted with anti-HA antibody. eEF2K co-IPed only when mGluR was coexpressed. Samples were boiled before loading to aggregate and separate mGluR5 monomer from eEF2K.
(E) mGluR1 co-IPs with eEF2K. HEK293T cells were transfected with mGluR1 and eEF2K, and lysates were IPed with mycAb. Samples were not boiled to show the monomer of mGluRs.
(F and G) mGluR2 and mGluR4 do not co-IP with eEF2K.