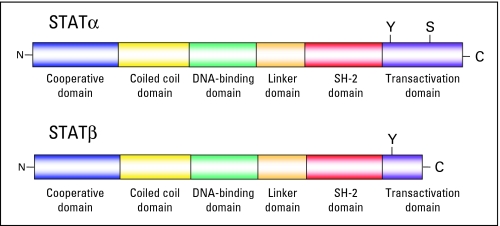
Fig 2.
Structure and functional domains of signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) molecules. Shown on the top is the full-length STATα. Below is the COOH-terminal (C) transactivation domain truncation resulting in STATβ isoforms. The following two phosphorylation sites in the COOH domain exist: a tyrosine phosphorylation site (Y) that controls dimerization yielding the DNA-binding activity of the STATs, and a serine phosphorylation residue (S) that further modulates the transcriptional activity of STATs.