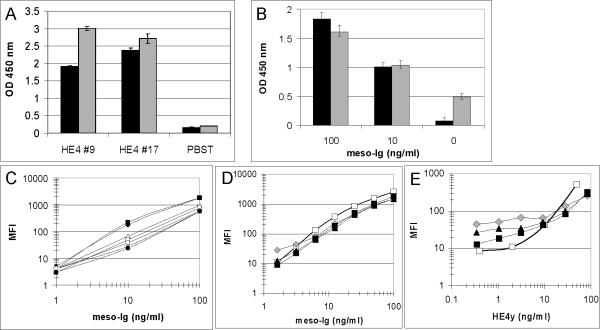
Figure 2. Development of Bb/pAb assays.
A, Validation of diploid-secreted biotinylated HE4 recombinant protein: Ni-purified b-HE4y was immobilized on a streptavidin plate and detected with 3D8 mAb (black bars) or 2H5 mAb (gray bars) followed by HRP-anti-mIg. As a negative control, wells were coated with PBST only; B, Comparison of anti-mesothelin Bbs’ ability to capture a mesothelin recombinant protein (meso-Ig): anti-mesothelin P4 (black bars) and P2 (gray bars) Bbs were immobilized on a streptavidin plate and incubated with serial dilutions of meso-Ig. Captured recombinant proteins were detected with HRP-anti-hIg; C, Optimization of anti-mesothelin Bb/pAb assay: anti-mesothelin pAb-coated fluorescent microspheres were incubated with serial dilutions of meso-7 in buffer. Captured proteins were detected with P4 Bb premixed with seven different types of modified fluorescent Streptavidin R-PE: black diamonds PJ31S; black squares PJLS; white triangles PJ35S; white squares PJ37S; stars PJ39S; white circles PJ33S and black circles SA-PE; D-E, Detection ranges of anti-mesothelin and HE4 Bb/pAb assays: anti-mesothelin (D) or anti-HE4 (E) pAb-coated fluorescent microspheres were incubated with serial dilutions of meso-Ig (D) or HE4y (E) recombinant proteins diluted in buffer (white squares) or in serial dilutions of NHS (20 fold, gray diamonds; 10 fold, black triangles; five fold, black squares). Captured proteins were detected with P4 Bb (D) or anti-HE4 Bb pool (E) premixed with PJ31S streptavidin.