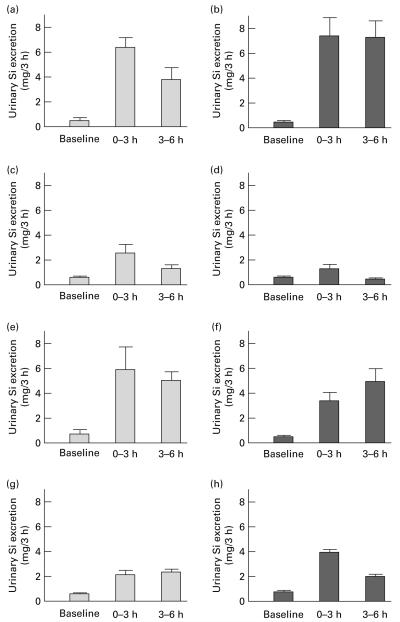
Fig. 3.
Urinary Si excretion (mg/3 h) over the 6 period following the ingestion of: (a) an orthosilicic acid (OSA) solution containing 21·4 mg Si (n 5); (b) alcohol-free beer containing 22·9 mg Si (n 5); (c) cooked green beans containing 6·1 mg Si (n 5); (d) ripe, peeled bananas containing 13·6 mg Si (n 5); (e) colloidal silica containing 780 mg Si (n 3); (f) magnesium trisilicate British Pharmacopoeia (BP) containing 200 mg Si (n 8); (g) choline-stabilised orthosilicic acid (ChOSA) containing 20 mg Si (n 8); (h) monomethyl silanetriol (MMST) containing 6·9 mg Si (n 14). Results are means, with standard errors represented by vertical bars (n 5-14, see Table 1). Si-containing supplements and products were ingested at the maximum dose recommended. The increase in urinary Si excretion (0-6 h) was statistically significant following the ingestion of OSA (P<0·0001), alcohol-free beer (P<0·001), green beans (P=0·04), magnesium trisilicate BP (P<0·001), ChOSA (P<0·001), MMST (P<0·001) and colloidal silica (P=0·03), but not following the ingestion of bananas (P=0·13).