Figure 1.
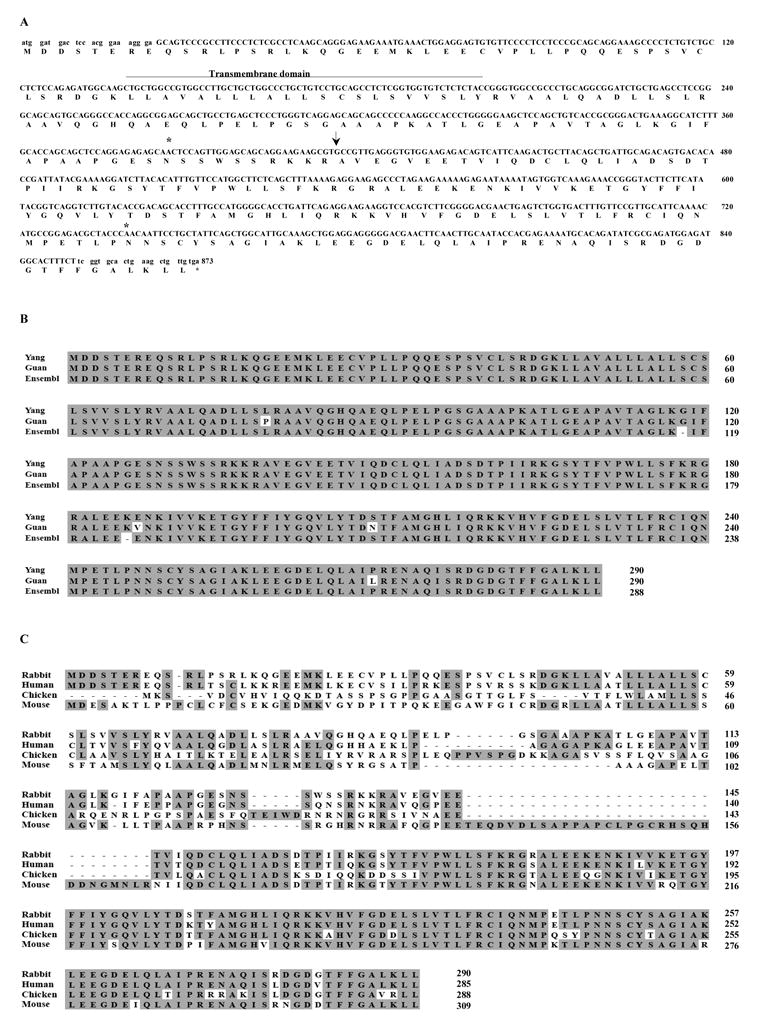
BAFF Sequences. (A) DNA and deduced protein sequences of rabbit BAFF. The predicted transmembrane domain (line), the potential N-glycosylation sites (stars), and the predicted natural processing site of rabbit BAFF (arrow) are indicated. Lowercase letters at the 3′ and 5′ ends indicate the location of the primer sequences used for initial PCR amplification. Our BAFF sequence was submitted to GenBank and given accession number EU982819. (B) Comparison of the predicted rabbit BAFF protein sequences from our study (Yang), reported paper (Guan) [29], and Ensembl (Ensembl). Identical residues are represented in black boxes. (C) Comparison of the BAFF protein sequences among different species. Identical residues are represented in shaded areas.
