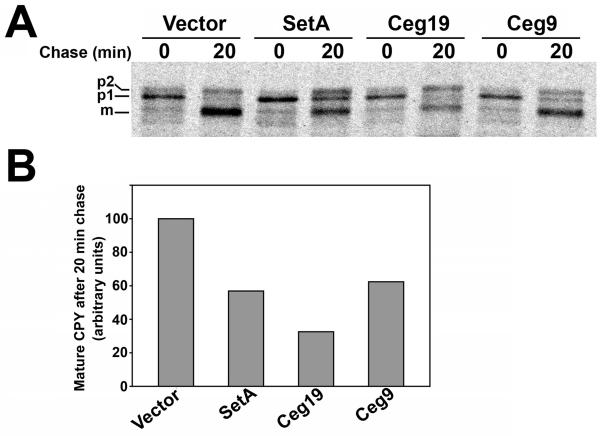
Fig. 4. Production of SetA, Ceg19 and Ceg9 cause distinct trafficking defects in yeast.
(A) Pulse-chase analysis of yeast expression strains. Yeast strains grown in the presence of 2% galactose were pulsed for 7 min with 35S-labeled cysteine/methionine to label nascent proteins and then chased for 20 min with excess unlabeled amino acids. Pulse-labeled CPY was immunoprecipitated, resolved on an 8% acrylamide gel, and visualized by autoradiography. The positions of mature and precursor forms of CPY are indicated on the left side of the autoradiogram. (B) Quantification of CPY trafficking defects in yeast strains producing SetA, Ceg19 and Ceg9. Mature CPY (mCPY) levels for each strain were visualized as described in (A) and quantified using densitometry. Levels were normalized to the mature CPY signal from the empty vector control strain and plotted as a bar graph. Data is representative of 2 separate experiments.