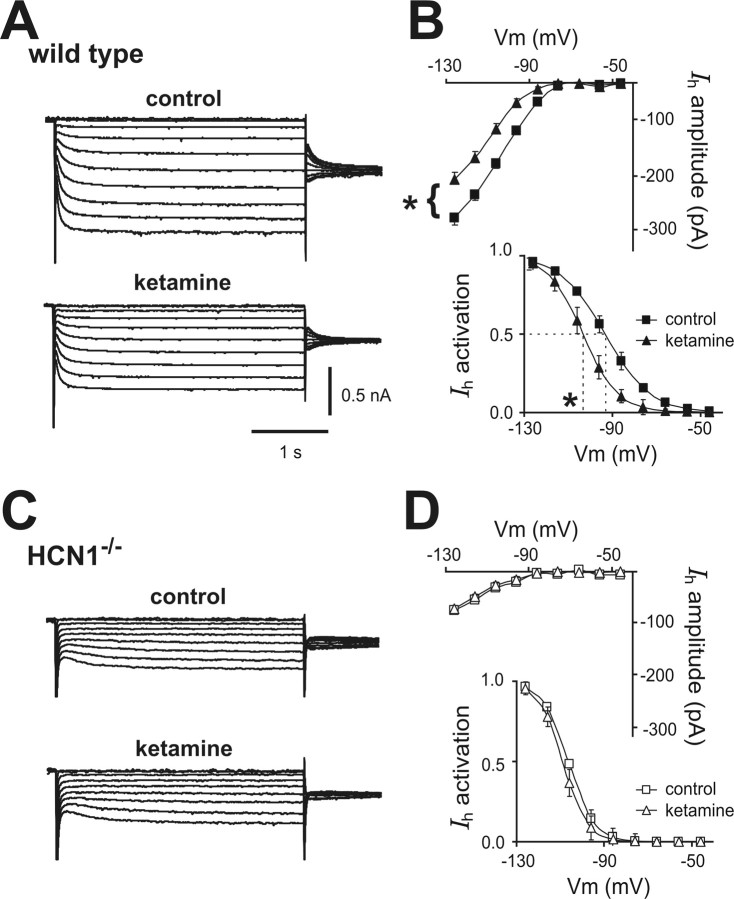
Figure 2.
Ketamine inhibits I h in cortical pyramidal neurons from wild-type mice, but not from HCN1 knock-out mice. A, C, Voltage-clamp recordings of I h in cortical pyramidal neurons from wild-type and HCN1 knock-out mice, under control conditions (top) and during exposure to ketamine (20 μm, bottom). B, D, Averaged steady-state I–V (top) and voltage dependence of I h activation (bottom) under control conditions (squares) and in the presence of ketamine (20 μm, triangles) in cortical pyramidal neurons from wild-type and HCN1−/− mice. Ketamine induced an approximately −10 mV shift in V½ of I h activation and an approximately 30% decrease in I h amplitude (at −128 mV) in cortical neurons from wild-type mice but had no effect on I h in HCN1 knock-out mice (ΔV½ approximately −2 mV; ∼5% inhibition). *p < 0.05 by paired t test; n = 5 each for wild type and HCN1 knock-outs. Vm, Membrane voltage.