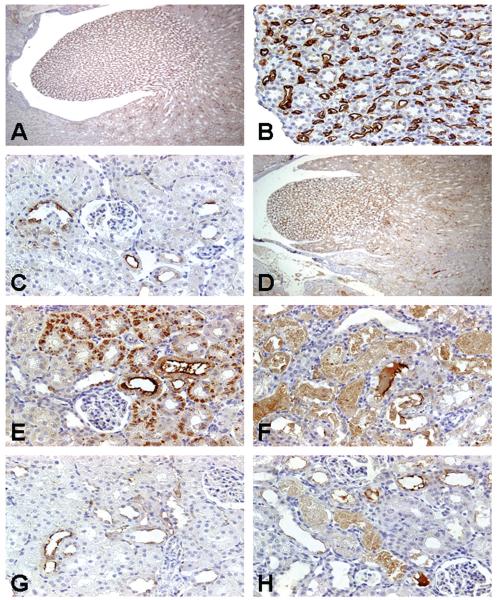
FIGURE 4.
Representative photomicrographs of renal papillary antigen-2 (RPA-2) immunoreactivity in kidneys of rats treated with nephrotoxicants. RPA-2 expression was located predominantly in the epithelial cells of the descending and ascending thin loop of Henle (LH) segments in the medulla (A) in control rats. The immunostaining for RPA-2 in control rats showed homogenous reaction within the cytoplasm of LH cells and intense reaction on their surfaces (B). Note the epithelial cells of medullary collecting ducts in the vicinity of RPA-2-expressing tubules were completely negative. RPA-2 expression was sporadic in the epithelial cells in the ascending thick LH segments of the cortex in control rats (C). Treatment of rats with gentamicin 100 mg/kg, sc, for 3 days did not change RPA-2 expression in the epithelial cells of the descending and ascending thin LH segments in the medulla (D) but resulted in new expression of RPA-2 in proximal tubular epithelial cells 24 hours (E) and 72 hours (F) after the last dose. There was no RPA-2 expression in the S1/S2 segments in mercury-treated rats (G). In contrast, RPA-2 expression was noted in the S1/S2 segments in chromium-treated rats (H). Original magnification of all figures: ×400, except figures (A, D, G), ×50.