Fig. 2.
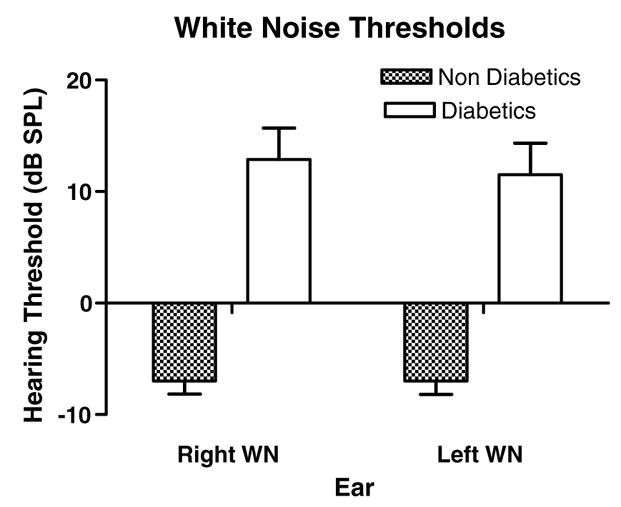
Diabetics showed a dramatic increase in white noise (WN) thresholds for both ears. Like pure tones, a greater difference was found for the right ear. ANOVA showed significant main effect for subject groups (p < 0.0001, F = 76.7, df = 1). Pairwise comparisons for each ear were also highly significant (right: p < 0.001, t = 6.42, df = 1; left: p < 0.001, t = 5.97, df = 1). Interactions were not significant. Error bars are SEM.
