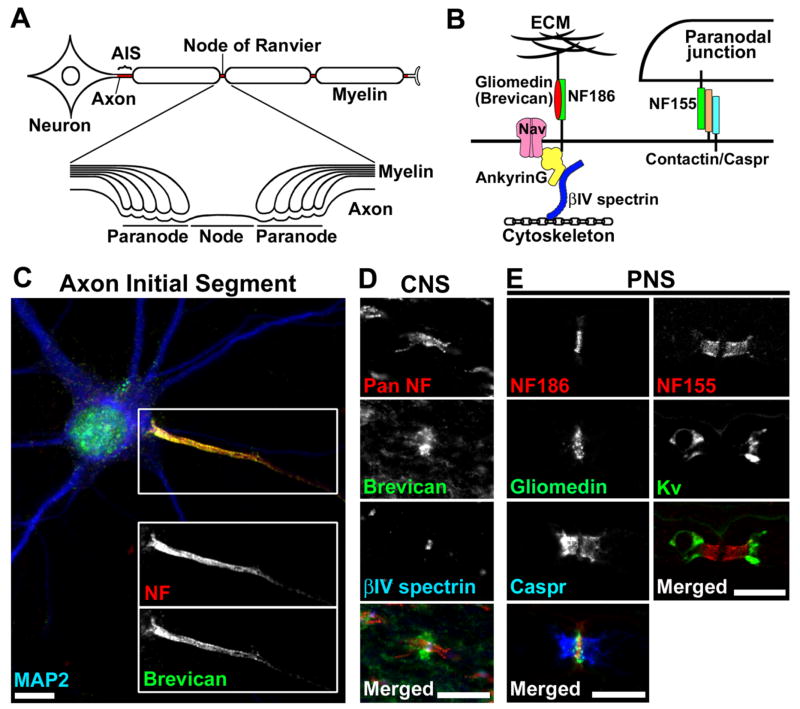
Figure 1.
(A) Cartoon illustrating the structures of the myelinated nerve fiber and the specific subdomains: AIS, nodes of Ranvier, and paranodes.
(B) Schematic presentation showing molecular organization at nodes and paranodes. At nodes, gliomedin (PNS) and brevican (CNS) are present at the ECM, and interact with NF186 at the nodal axolemma. A scaffolding protein ankyrinG interacts with NF186, Nav channels, and the cytoskeletal protein βIV spectrin. At paranodes, axonal Caspr and contactin, and glial NF155 form a tripartite CAM complex, and mediate assembly of the septate-like junctions between the myelin sheath and the axon.
(C) NF (red) and brevican (green) are highly accumulated at the AIS in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. The somatodentritic domain is characterized by the staining of microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2; blue). Scale bar = 10 μm.
(D) Pan NF antibody (red) labels both node and paranode in rat optic nerve. Brevican (green) is localized at and around nodes of Ranvier in the ECM. Nodes are shown in blue by anti-βIV spectrin antibody. Scale bar = 10 μm.
(E) Nodal and paranodal components in the PNS. Left column shows rat sciatic nerve stained by antibodies to NF186 (red), gliomedin (green), and Caspr (blue). The short gap between two Caspr clusters is filled with nodal NF186 staining. Note that the gliomedin staining extends outside of the nodal NF186 staining. The right column shows mouse ventral root stained by antibodies to NF155 (red) and Kv channels (green). Note the nodal gap between the two paranodal NF155 clusters. Scale bars = 10 μm.