Figure 1.
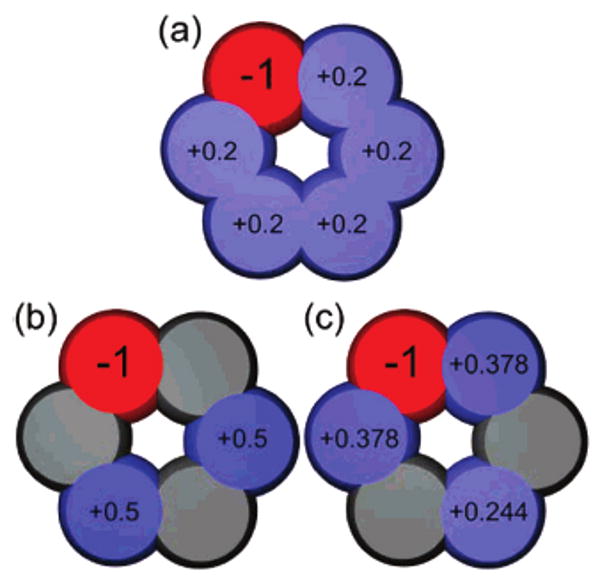
Different charge distribution schemes used, for the hexagon. Shown are example charge distributions for the N-bracelet case, where the large charge is negative (red). In the distributed scheme (a), neutralizing charge is distributed equally across all of the remaining atoms. In the opposing scheme (b), neutralizing charges of 0.5 are placed on the two atoms as far away as possible away from the atom with the largest charge. In the fixed dipole scheme (c), charges are distributed to keep the dipole moment fixed to that for the triangle. Atoms are color coded by magnitude of the charge, with red for negative, blue for positive, and gray for neutral.
