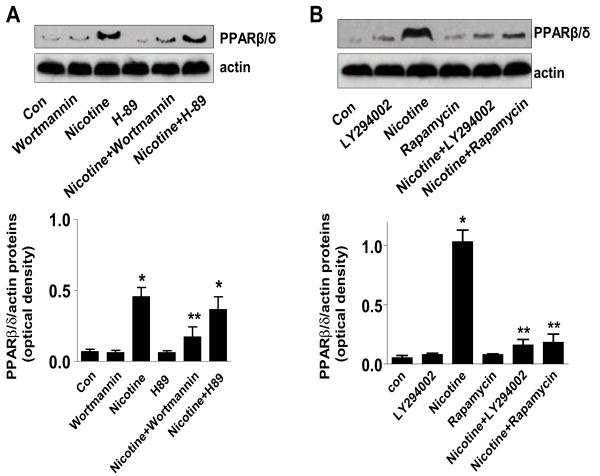
Figure 3. Involvement of Akt and mTOR in the induction of PPARβ/δ expression by nicotine.
A, Protein was isolated from H1838 cells treated with LY294002 (25 μM) or rapamycin (20 nM) for 2 h before exposure to nicotine for an additional 24 h. Afterwards, Western blot analysis was performed using anti-PPARβ/δ antibodies. B, Protein isolated from H1838 cells treated with Wortmannin (0.2 μM) or H89 (10 μM) for 2 h before exposure to nicotine for an additional 24 h was assayed by Western blot using anti-PPARβ/δ antibodies. Each bar (lower panel) represents the mean ± SD of PPARβ/δ/actin of at least three independent experiments. * indicates significant difference from untreated control. ** indicates significance of combination treatment as compared with nicotine alone. Con, untreated control cells.