Figure 6.
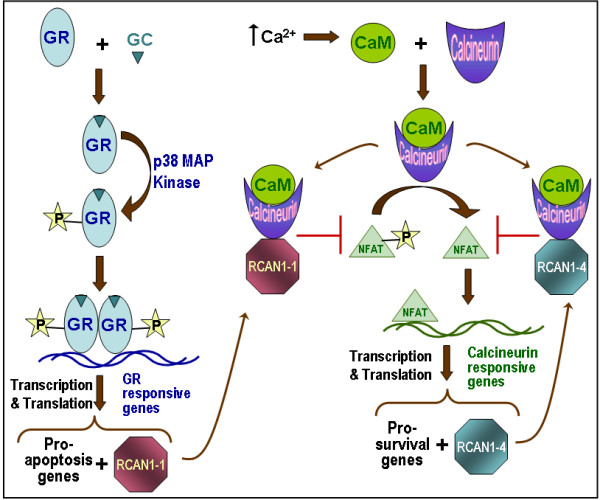
RCAN1 mediated regulation of cell proliferation and apoptosis: Schematic shows that GC-dependent GR activation and subsequent MAP kinase-dependent phosphorylation enables GR binding to GRE sequences on target genes. GR alters expression profiles of T-lymphoid cells resulting in a net increase in pro-apoptotic gene expression. One of the gene that GR induces is RCAN1-1. Increases in [Ca2+]i levels triggers the calcium signaling pathway, culminating in the activation of calcineurin phosphatase (PP3C), which dephosphorylates and activates NFAT, causing its nuclear translocation. NFAT induces transcription of pro-survival genes, and RCAN1-4, which serves as a negative feed-back regulatory loop, because it can directly bind to and inactivate calcineurin phosphatase. GR-dependent induction of RCAN1-1 also causes inhibition of calcineurin, and subsequent down-regulation of pro-survival genes, thus facilitating GR-dependent apoptosis of T lymphoid cells.
