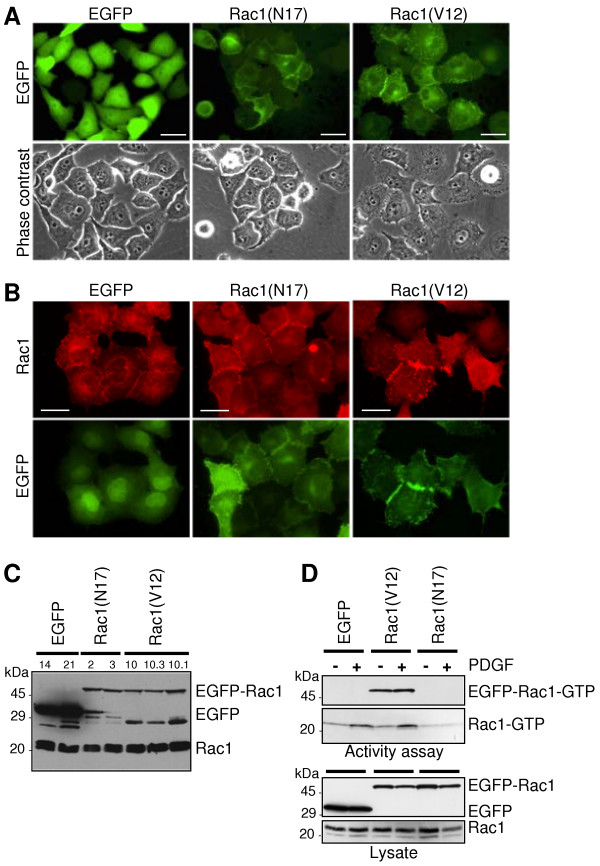
Figure 1.
Expression of EGFP-Rac1(V12) and EGFP-Rac1(N17) in PANC-1 cells. (A) Localisation of EGFP-Rac1(V12) and EGFP-Rac1(N17). EGFP fluorescence (upper panel) and phase contrast analyses (lower panel) demonstrate the localisation of EGFP proteins and the morphology of subconfluent, living PANC-1 cells stably expressing EGFP, EGFP-Rac1(V12) and EGFP-Rac1(N17), bar = 20 μm. (B) Immunofluorescence analysis of Rac1 localisation. Fixed EGFP-, EGFP-Rac1(V12)- and EGFP-Rac1(N17)-expressing cells were incubated with Rac1-specific antibody. EGFP fluorescence is illustrated for comparison (bar = 30 μm). (C) Expression of EGFP, EGFP-Rac1 and endogenous Rac1 in 30 μg of total cell lysate of different cell clones was estimated by Western blotting using Rac1- and GFP-specific antibodies. One representative blot of three independent experiments is shown. (D) The amount of active Rac1-GTP in EGFP- and EGFP-Rac1-expressing cells was determined by affinity precipitation assays (upper panel). The cells were serum-starved for 24 h and then left untreated (-) or treated with 10 ng/ml PDGF AB for 5 min (+). The assay was performed with 500 μg (Rac1) or 1000 μg (EGFP-Rac1) of cell lysate. To control for equal loading, aliquots of the samples were analysed in parallel in Western blotting (lower panel). One representative blot out of three independent experiments is shown.