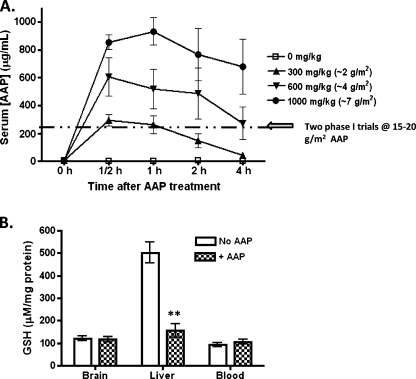
Figure 5.
In vivo studies of AAP pharmacokinetics and AAP effect on cellular GSH levels. (A) Levels of AAP in the serum of rats (n = 5 per group) administered 0, 300, 600, or 1000 mg/kg (0, 2, 4, and 7 g/m2, respectively) AAP IP at times 0, 0.5, 1, 2, and 4 hours as measured using a direct ELISA test. Data were expressed as mean ± SEM. The dashed line indicates the peak levels of AAP measured in the serum of human patients during two phase 1 toxicity trials in which the patients were administered 15 to 20 g/m2 AAP [16,36]. (B) Rats were administered an IP dose of either vehicle or AAP at 1000 mg/kg. The rats were allowed to recover, and the liver, the brain, and whole blood were harvested for GSH levels at 6 hours after treatment (B). Statistical significance between treatment (+AAP) and control (No AAP) group was indicated by asterisks: **P < .01.