Figure 8.
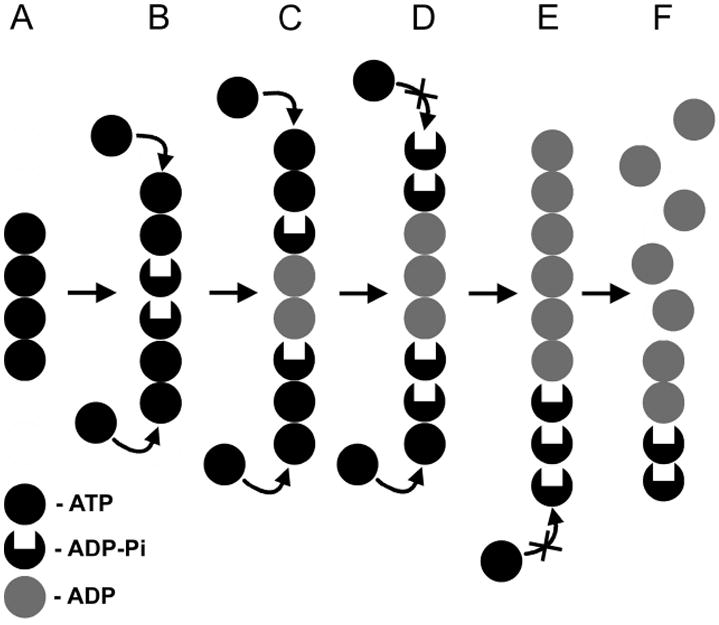
Model for the dynamic instability of ParM filaments. ParM filament is shown as a stack of circles, where each circle represents a ParM protomer. Black circles represent ParM-ATP; grey circles represent ParM-ADP, and black circles with deleted center stand for the intermediate ParM-ADP-Pi state. Shortly after polymerization ParM filament is comprised of ATP subunits (A), which over time turn into ADP-Pi state (B) followed by the ADP state (C). The integrity of the filament in (A-C) is preserved by the ATP-cap. Inorganic phosphate release inhibits the formation of the protective ATP-cap (D). Finally, the ADP subunits are exposed (E), and the filament depolymerizes (F).
