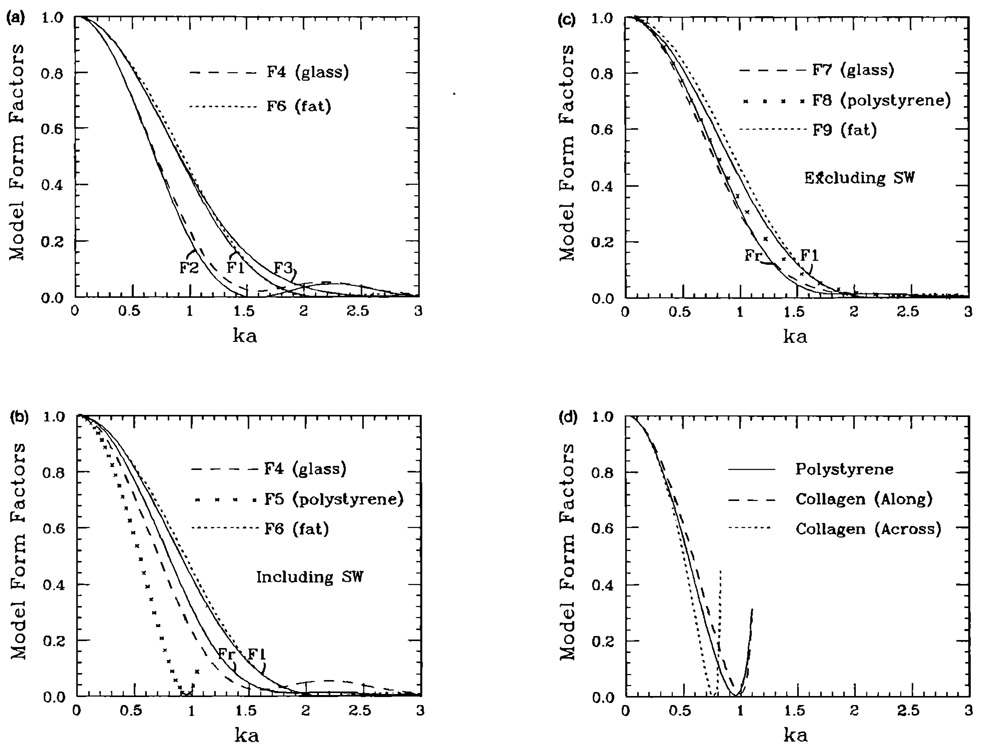
FIG. 2.
(a) Form factors for the fluid sphere model F1, the spherical shell model F2, and the Gaussian model F3; F4 and F6 are form factors calculated from the Faran scattering theory13 for microspheres made of glass and fat, respectively. (b) Form factor for the rigid, immovable sphere Fr is plotted along with the fluid sphere model F1 (solid lines) and that calculated for glass, polystyrene, and fat microspheres from the Faran scattering theory.13 These data include the effects of shear waves generated inside the particle. (c) Same as (b), except that the glass, polystyrene, and fat data are calculated from the theory of Morse and Ingard.9 These results do not include the effects of shear waves. (d) Form factors for collagen along and across the fibers. The results are computed using the Faran theory and the parameters are taken from the work of Cusak and Miller.17 These results show that scattering from collagen spheres may be approximated by that of polystyrene.