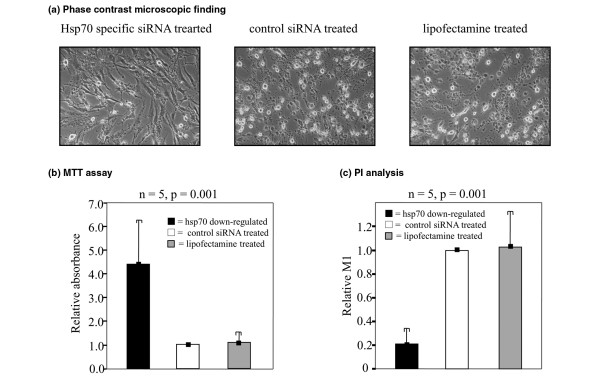
Figure 2.
Effect of heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) knock-down on nitric oxide-induced apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs). To induce apoptosis, cells were treated with 1 mM sodium nitroprusside (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) for 24 hours in a light-shielded state. The cytoprotective effect of Hsp70 knock-down was observed by phase-contrast microscopy (a). MTT assays showed that cell viability was significantly greater in Hsp70 downregulated FLSs (left) than in control FLSs (middle = control small interfering RNA [siRNA]-treated cells, right = lipofectamine-treated cells) (mean of relative absorbance, 4.39 ± 2.82 versus 1.00 ± 0.00 versus 1.09 ± 0.30, P = 0.001 by analysis of variance [ANOVA]) (b). Propidium iodide (PI) analysis showed that the apoptotic fraction in Hsp70 downregulated FLSs (left) was significantly lower than in control FLSs (middle = control siRNA-treated cells, right = lipofectamine-treated cells) (mean of relative M1, 0.21 ± 0.16 versus 1.00 ± 0.00 versus 1.03 ± 0.36, P = 0.001 by ANOVA) (c). All experiments were performed in triplicate using five RA FLS samples. The histograms and error bars indicate mean and standard deviation of relative absorbance, respectively. MTT, 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide.