Figure 1.
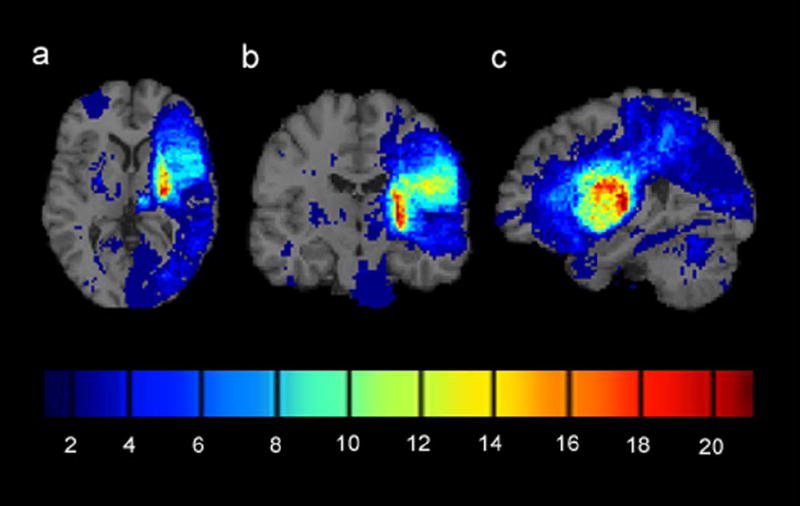
Infarct overlap map for 81 chronic stroke patients with mild to moderate upper extremity hemiparesis. Brains of patients with right arm hemiparesis were flipped left to right to equate for deficit side. (a) Axial cross-section through the basal ganglia. (b) Coronal cross-section through the primary motor area. (c) Sagittal cross-section through the medial temporal lobe. The colorbar indicates the number of patients with infarcts at each voxel. Infarcts were most frequently observed in the posterior limb of the internal capsule contralateral to the side of motor deficit (colored red).
