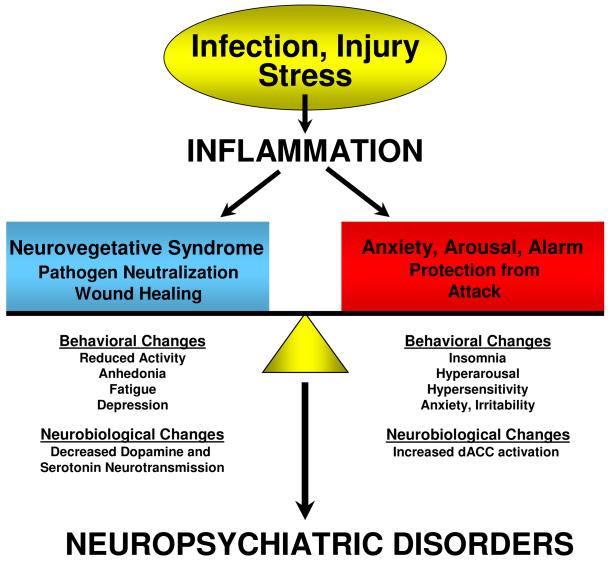
Figure 3. The Contribution of the Neurovegetative Syndrome and Anxiety, Arousal and Alarm to Cytokine-Induced Neuropsychiatric Disorders.
Cytokine-induced inflammatory responses lead to a host of behavioral changes that can be grouped into 1) a “neurovegetative syndrome” that subserves shutting the organism down to facilitate fighting infection and would healing and 2) an “anxiety, arousal and alarm state” that subserves protection against future attack. These behavioral responses are mediated by the impact of cytokines on relevant neurobiological pathways and represent a reorganization of behavior to address competing survival priorities, the balance of which will determine the clinical manifestations of related cytokine-induced neuropsychiatric disorders.