Figure 1.
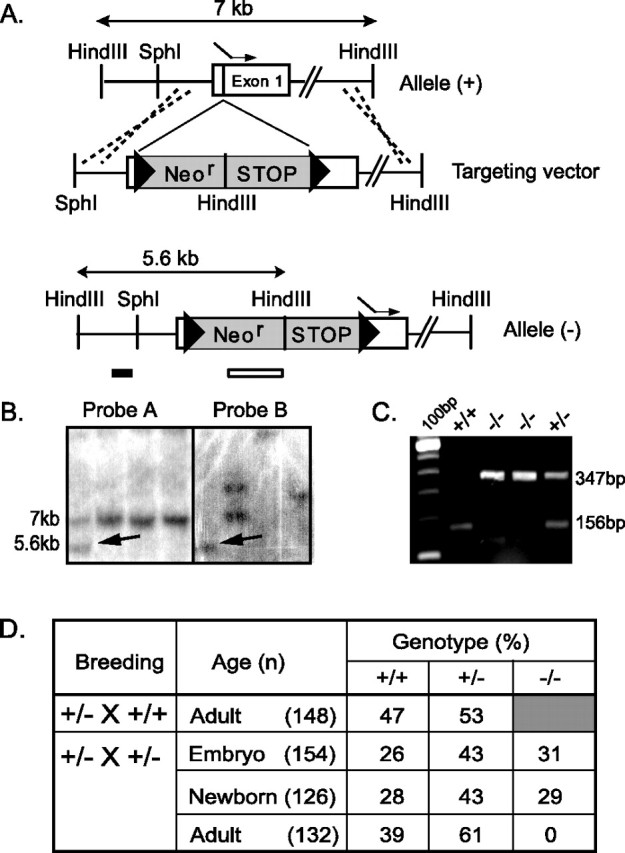
Targeted disruption of the mouse GLS1. A, Schematic representation of the GLS1 genomic DNA [allele (+)] and disrupted gene [allele (−)]. A targeting vector was constructed by introducing a cassette (gray box) containing a neomycin resistant (Neor) and a STOP sequence, flanked by two loxP sites (triangles), upstream of the ATG initiating codon (dashed arrow) in the first exon (white box). B, Southern blot analysis of ES cell clones. After digestion of ES cell DNA by HindIII, probe A (GLS1 probe) hybridized to a 5.6 kb band for the mutant allele (arrow) and a 7.0 kb band for the wild-type allele (+); probe B (neo probe) hybridized when homologous recombination occurred to a 5.6 kb band for the mutant allele (arrow). C, PCR GLS1 genotyping. Mice were genotyped using a three-primer PCR strategy (two primers in the wild-type sequence, one in the mutant cassette). The wild-type allele yielded a 156 bp band, and the targeted allele yielded a 347 bp band. D, Genotypic distribution of offspring of GLS1 mutants. Embryos were genotyped at E17–E18, newborns were genotyped at birth, and adults were genotyped at 1–3 weeks of age (n = number of animals). GLS1−/− pups died at P0.
