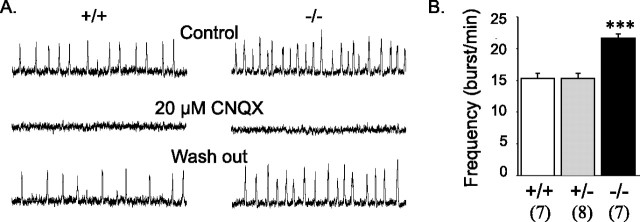
Figure 9.
Rhythmic activity generated by the respiratory neural network in vitro in coronal brainstem slices. A, Integrated population activity recorded in preparations obtained from wild-type (+/+) and null (−/−)mutants in control conditions (top traces) after blockade of glutamatergic connections (middle traces) and after wash out (bottom traces). Bath application of 20 μm CNQX abolished spontaneous rhythmic activity in both wild-type and null mutant slices. B, Mean frequency of rhythmic activity. There was a significant increase in respiration-associated burst frequency in null mutant slices (−/−). Numbers of animals are indicated in parentheses. ∗∗∗p < 0.001 nulls versus wild type and heterozygotes. Error bars represent SEM.