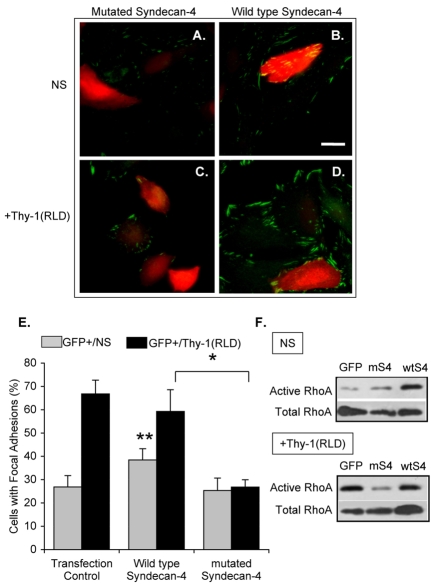
Fig. 5.
Transfection of astrocytes with a syndecan-4 mutant lacking the cytoplasmic domain decreases Thy-1-stimulated focal-adhesion formation. Cells were transiently co-transfected with EGFP-containing plasmid and either truncated (A,C) or wild-type (B,D) syndecan-4. DI TNC1 astrocytes were then left unstimulated (NS; A,B) or were stimulated with Thy-1(RLD)-Fc-beads [+Thy-1(RLD); C,D]. Samples were analyzed by immunofluorescence using mouse anti-paxillin antibodies followed by Cy3-labeled anti-mouse IgG. Red and green colors were inverted to improve visualization of focal adhesions; therefore, in images obtained using confocal microscopy, focal adhesions are in green in both non-transfected (no color) and GFP-transfected (red) cells. Scale bar: 25 μm. (E) Quantification of cells with focal adhesions within the transfected cell population in each transfection condition (GFP+) is shown for non-stimulated (gray bars) and Thy-1-stimulated cells (black bars). Cells with focal adhesions were evaluated as indicated in Fig. 4. Values were obtained by evaluating at least 100 GFP-positive cells per condition from three independent experiments. Statistically significant differences are indicated between values obtained for wild-type syndecan-4 with either transfected control (**P<0.05) or mutated syndecan-4 (*P<0.05). (F) Transfected DI TNC1 cells were serum-starved overnight and then stimulated or not (NS) for 15 minutes with Thy-1-Fc-beads [+Thy-1(RLD)]. The cells were then lysed and active RhoA was affinity-precipitated with RBD-GST-beads. RhoA was visualized by immunoblotting as indicated in Fig. 1A. A representative result from three independent experiments is shown.