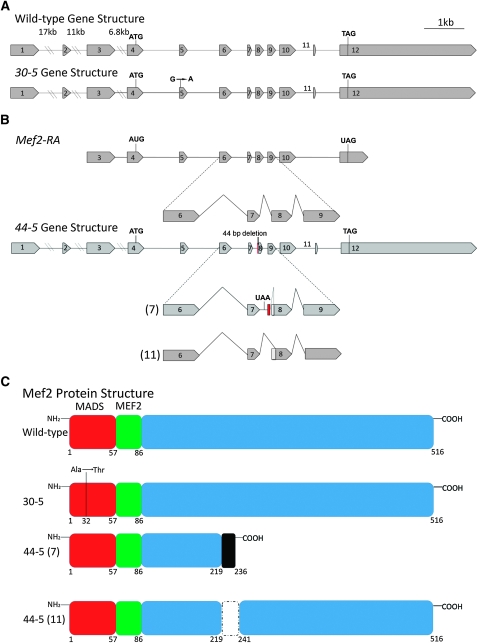
Figure 2.—
Gene structure, splicing patterns, and protein structure in Mef2 wild-type and mutant alleles. (A) Gene structure of wild type and 30-5. 30-5 contains a G-to-A point mutation in exon 5. (B, top) The wild-type Mef2-RA isoform represents one of the predominant Mef2 transcripts, the designation for which is from FlyBase (http://flybase.org). A detailed view of its splicing pattern between exons 6 and 9 is also shown, compared to the 44-5 gene structure and its two alternative splicing patterns. The 44-5 allele contains an additional 9 bp of nucleotides following intron 7 (shown in red) and 44 bp of nucleotides deleted from the 5′ end of exon 8, including the normal exon 8 splice acceptor. The 44-5 (7) cDNA retains intron 7, which includes a premature stop codon (UAA), and cryptically splices into the 45th bp of exon 8. The 44-5 (11) isoform utilizes the normal 5′ splice donor of exon 7, but splices cryptically into the 52nd bp of exon 8. (C) Wild-type MEF2 contains a 57-amino-acid MADS DNA-binding domain, and a 29-amino-acid MEF2 DNA-binding and dimerization domain. 30-5 contains an alanine-to-threonine substitution at amino acid 32. The black shaded box of 44-5 (7) is translated intron sequence and contains a premature stop codon at amino acid 236. 44-5 (11) contains an internal deletion of amino acids 219–241.