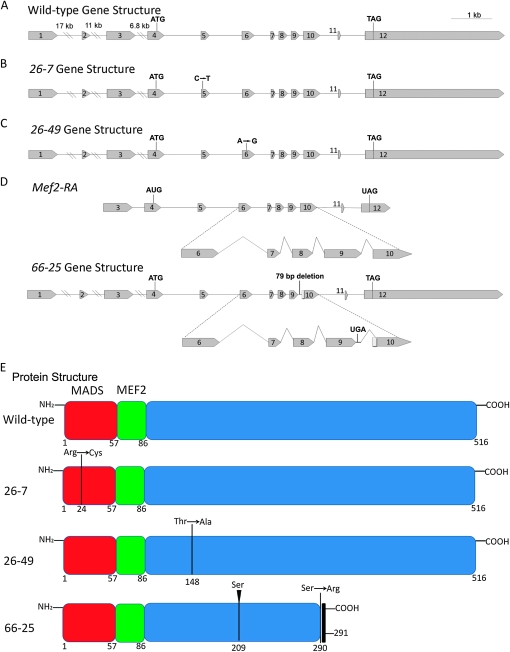
Figure 7.—
Analysis of gene and predicted protein structure for three new Mef2 mutant alleles. (A) Wild-type gene structure contains 12 exons. The ATG start codon is in the 4th exon and the TAG stop codon is in the 12th exon. (B) The 26-7 allele has a point mutation from C to T in exon 5, encoding an amino acid change from arginine to cysteine at amino acid 24. (C) The 26-49 allele has a point mutation from A to G in exon 6, encoding an amino acid change from threonine to alanine at amino acid 148. (D) The normal splicing pattern is shown for the Mef2-RA isoform. The 66-25 mutation is a 79-bp deletion after exon 9, which deletes the splice acceptor site and causes the gene to read into the intron and splice cryptically into the 10th exon. The result is to encode a stop codon 1 amino acid after the 9th exon. This allele also has an insertion of a serine codon after codon 209 (not shown on gene structure). (E) Predicted protein structure for wild-type and three new Mef2 mutant alleles as indicated: the 26-7 mutation encodes an amino acid change from arginine to cysteine at amino acid 24, which occurs in the DNA-binding MADS domain; the 26-49 mutation encodes an amino acid change from threonine to alanine at amino acid 148, which occurs in the downstream C-terminal region; the 66-25 mutation encodes an insertion of serine at amino acid 209 and a premature stop arising from readthrough of intron 9.