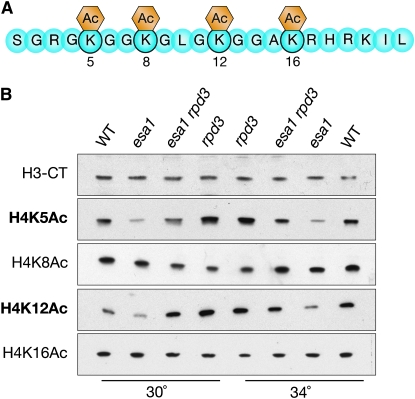
Figure 5.—
Deletion of RPD3 restores global acetylation levels of specific histone H4 residues in esa1 mutants. (A) Diagram of the histone H4 N-terminal tail highlighting sites of acetylation modifications. (B) Deletion of RPD3 restored global acetylation of H4K5 and H4K12, but not H4K8 and H4K16. Whole cell protein extracts from wild-type (LPY5), esa1 (LPY4774), esa1 rpd3 (LPY12156), and rpd3 (LPY12154) cells at both permissive (30°) and restrictive (34°) temperatures were immunoblotted with an antiserum specific to the C terminus of H3 to control for histone levels, and with H4 antisera to detect the amount of bulk histone acetylation at each lysine residue.