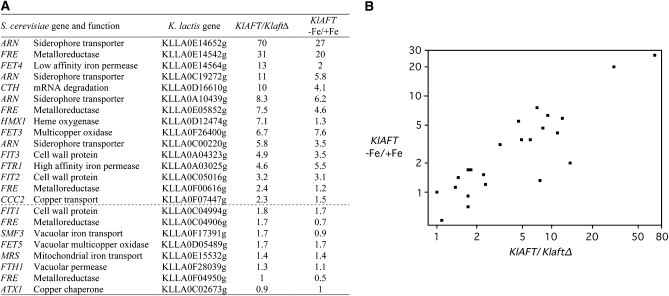
Figure 3.—
KlAft- and iron-dependent expression of K. lactis homologs of S. cerevisiae Aft1/Aft2 iron-regulated genes. For the KlAFT/KlaftΔ comparison, the wild-type and KlaftΔ mutant cultures were grown in Bio101 minus iron and copper. For the KlAFT (−Fe/+Fe) comparison, wild-type cultures were grown in Bio101 minus iron and copper with (+Fe) or without (−Fe) ferric ammonium sulfate (100 μm). Expression of K. lactis genes was assessed by quantitative real-time PCR. The values shown are the KlAFT/KlaftΔ and the KlAFT (−Fe/+Fe) ratios calculated as the means of two independent experiments, each performed in duplicate. Standard deviations were <10%. (A) The first column contains the corresponding S. cerevisiae homolog gene or family name and the associated protein function. The second column contains the ORF name for the K. lactis genes analyzed. The group of genes for which the mRNA is at least twice as abundant in the wild type as in the KlaftΔ mutant is underlined with a dashed line. (B) −Fe/+Fe in the wild-type strain (y-axis on a logarithmic scale) is plotted against KlAFT/KlaftΔ (x-axis on a logarithmic scale). The transcription profiles obtained for the two comparisons were correlated with Spearman's rho coefficient = 0.83 and P-value <0.0001.