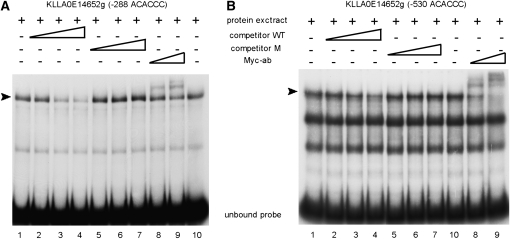
Figure 5.—
DNA binding of KlAft to the −288 ACACCC (A) and −530 ACACCC (B) sequences of the KLLA0E14652g promoter. Gel-shift assays were carried out with extracts from KlaftΔ (MLK53) cells expressing the KlAft-13Myc fusion protein. The radiolabeled probes used to perform the gel-shift assays correspond to the sequences of positions −382 to −251 and −570 to −429 of KLLA0E14652g (A and B, respectively). The arrowhead indicates the KlAft-containing complexes. Competitive assays were performed with excess oligonucleotide centered on the wild-type (competitor WT) ACACCC sequence (lanes 2–4) and mutant (competitor M) ACAGGG sequence (lanes 5–7). Where indicated, 1 and 2 μl of a monoclonal antibody raised against the Myc epitope were added (lanes 8 and 9, respectively).