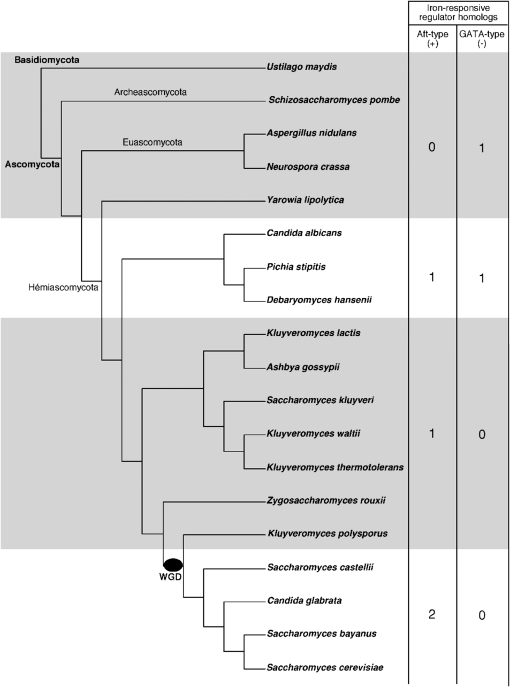
Figure 7.—
Evolution of iron-responsive transcription regulators in ascomycota. The species tree of ascomycota with the basidiomycota Ustilago maydis as the outgroup was adapted from Fitzpatrick et al. (2006) and Souciet et al. (2009). The S. castellii location in the tree (outgroup to the clade containing C. glabrata and S.cerevisiae) is supported by shared rearrangement data (Gordon et al. 2009). The whole-genome duplication is indicated with a black oval. The numbers in the table correspond to the number of homologs of iron-responsive transcription regulator-encoding genes per genome. The Aft-type proteins were identified by similarity with the Pfam transcription factor Aft domain (PF08731) and the GATA-type proteins were identified with the cysteine-rich domain of the Zn-finger GATA-type repressors (see materials and methods and File S2 and File S3).