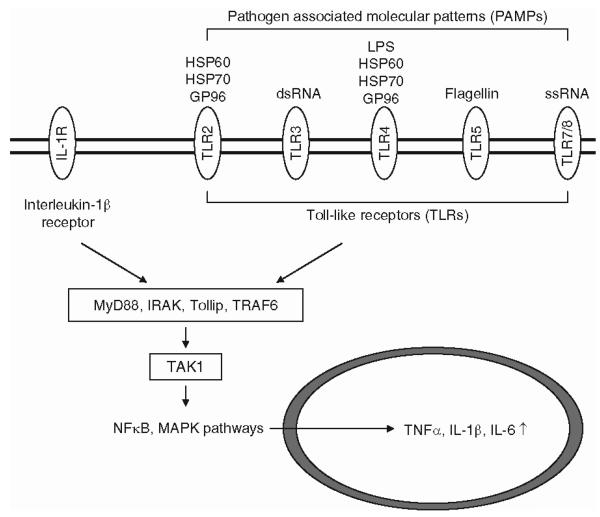
Fig. 2.
The Toll-like receptor (TLR) pathway. TLR activation initiates the innate immune response, which is thought to lead to the detrimental cytokine cascade in chronic pain. Activation of TLR signaling proceeds via a family of adaptor proteins which includes the protein MyD88, the interleukin-1 receptor associated kinase, Toll interacting protein, and the adapter protein TRAF6. These proteins activate the kinase TAK1, which ultimately leads to the activation of signaling cascades including nuclear factor κB and mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways. The activation of these pathways can then direct the synthesis of cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and interleukin-6 (IL-6). Both TLRs and receptors for IL-1β have similar structures and share a cytoplasmic motif. Activation of both types of receptors recruits a scaffolding complex that leads to upregulation of the production of similar cytokines