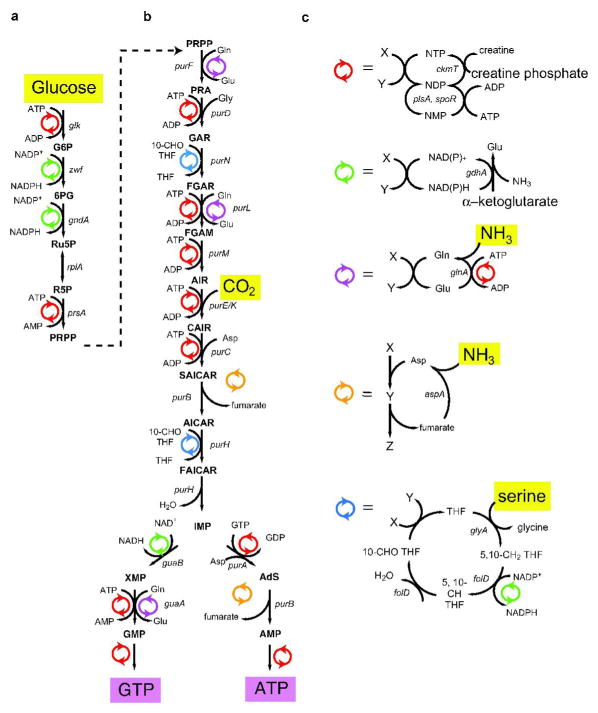
Figure 1. Scheme for Enzymatic Synthesis of Purine Nucleotides.
a) Conversion of Glucose to PRPP. Glucose and ATP are converted to glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) by the action of glucokinase (glk) with the production of ADP. G6P and NADP+ is converted to 6-phosphogluconate (6PG) by glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (zwf) with the production of NADPH. 6PG and NADP+ is converted to ribulose-5-phosphate (Ru5P) by the action of 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (gndA) with the production of NADPH. Phosphoriboisomerase (rpiA) interconverts Ru5P and ribose-5-phosphate (R5P). R5P and ATP are converted to phosphoribose-pyrophosphate (PRPP) by the action of PRPP synthase (prsA) with the production of AMP. b) Conversion of PRPP to ATP or GTP. PRPP and glutamine are converted to phosphoribose-amine (PRA) by the action of amidophosphoribosyl-transferase (purF) with the production of glutamine. PRA, glycine and ATP are converted to phosphoribosyl-glycinamide (GAR) by the action of phosphoribosylamine-glycine ligase (purD) with the production of ADP. GAR and 10-formyl-tetrahydrofolate are converted to phosphoribosyl-formylglycinamide (FGAR) by the action of phosphoribosyl-glycine amide formyltransferase (purN) with the production of tetrahydrofolate (THF). FGAR, glutamine and ATP are converted to phosphoribosyl-formylglycinamidine (FGAM) by the action of FGAM synthase (purL) with the production of glutamate and ADP. FGAM and ATP are converted to phosphoribosyl-aminoimidazole (AIR) by phosphoribosyl-formyl glycinamidine cyclo-ligase (purM) with the production of ADP. AIR, CO2 and ATP (47) are converted to phosphoribosyl-amino-carboxy-imidazole (CAIR) by the action of phosphoribosyl-amino-imidazole carboxylase (purE, purK) with the production of ADP. CAIR, aspartate and ATP are converted to phosphoribosyl-amino-succinocarboxamide-imidazole (SAICAR) by phosphoriobsyl-aminoimidazole-succino-carboxamide synthase (purC) with the production of ADP. SAICAR is converted to phosphoribosyl-amino-imidazole carboxamide (AICAR) by adenylosuccinate lyase (purB) with the production of fumarate. AICAR and 10-formyl-THF are converted to phosphoribosyl-formylamido-imidazole carboxamide (FAICAR) by the action of phophoribosylamino-imidazole-carboxamide formyltransferase (purH) with the production of THF. FAICAR is converted to inosine monophosphate (IMP) by IMP cyclohydrolase (purH) with the production of H2O. For ATP: IMP and GTP are converted to adenylosuccinate (AdS) by adenylosuccinate synthase (purA) with the production of GDP. AdS is converted to AMP by the action of purB with the production of fumarate. For GTP: IMP and NAD+ are converted to xanthosine monophosphate (XMP) by the action of IMP dehydrogenase (guaB) with the production of NADH. XMP, glutamine and ATP are converted to GMP by the action of GMP synthase (guaA) with the production of AMP and glutamate. c) Cofactor Regeneration Schemes. NTP Regeneration (Red). AMP and ATP are converted to ADP by the action of adenylate kinase (plsA). GMP and ATP are converted to GDP by the action of guanylate kinase (spoR) with the production of ADP. NDP’s and creatine phosphate are converted to NTP’s by the action of creatine phosphokinase (ckmT) with the production of creatine. Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Regeneration (Green). NAD(P)H, α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) and NH3 are converted to NAD(P)+ by the action of glutamate dehydrogenase (gdhA) with the production of glutamate. Glutamine Recycling (Purple). Glutamate, ATP and NH3 are converted to glutamine by the action of glutamine synthase (glnA) with the production of ADP. Aspartate Recycling (Orange). Fumarate and NH3 are converted to aspartate by the action of aspartate ammonia-lyase (aspA). Folate Regeneration (Blue). THF and serine are converted to 5,10-CH2-THF by the action of glycine hydroxymethyl-transferase (glyA) with the production of glycine. 5,10-CH2-THF and NADP+ is converted to 5,10-CH-THF by the action of methylene-THF dehydrogenase (folD) with the production of NADPH. 5,10-CH-THF is converted to 10-CHO (formyl) THF by the action of methenyl-THF cyclohydrolase (folD) with the production of H2O.