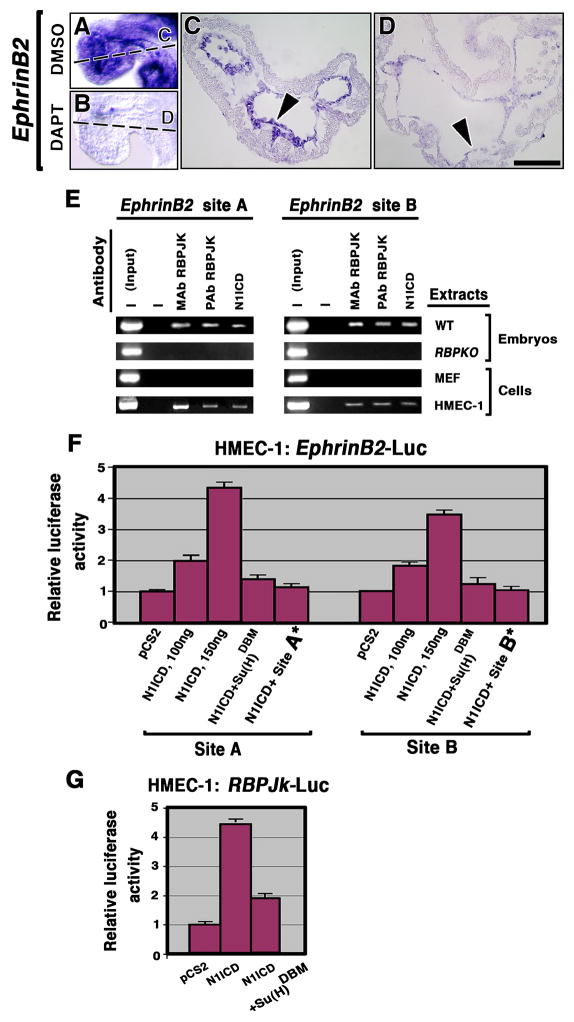
Figure 6. EphrinB2 is a Notch target in the endocardium.
(A–D) WISH showing EphrinB2 expression in E9.5 DMSO control (A, C, arrowhead) and severe reduction in DAPT-treated embryos (B, D, arrowhead). (E) ChIP assays. Chromatin from E9.5 wt and RBPJk mutant hearts, MEF and HMEC-1 cells was immunoprecipitated with monoclonal (MAb) or polyclonal (PAb) antibodies against RBPJK or N1ICD. The EphrinB2 genomic DNA was analyzed for RBPJK binding sites A and B. “Input” corresponds to PCR products generated using DNA from non-immunoprecipitated chromatin as a template. —, no antibody was added to the reaction mixture. (F) Luciferase reporter assays. HMEC-1 cells were co-transfected with Renilla luciferase plasmid and 100 or 150ng of N1ICD, Su(H)DBM effector plasmid or a control plasmid (empty pCS2 vector), in combination with a reporter plasmid containing wt RBPJK binding sites (A or B) or mutated ones (A* or B*). (G) HMEC-1 cells transfected with empty vector, N1ICD or Su(H)DBM and RBPJk reporter plasmid. After normalization to Renilla luciferase activity, firefly luciferase activity relative to that of control plasmid was calculated for each reporter. Relative values (mean+SD) from at least four independent experiments performed in triplicate are represented by the bars in the bar chart. Scale bar, 25 μm (C, D).